Astronomy

Astrophysics
Astrophysics is a branch of astronomy that applies the principles of physics and chemistry to understand the nature of celestial bodies and cosmic phenomena. It encompasses the study of the Sun, stars, galaxies, exoplanets, the interstellar medium, and the cosmic microwave background, analyzing their luminosity, density, temperature, and chemical composition.

Aurora Borealis
The Aurora Borealis, or Northern Lights, is a natural light display predominantly seen in high-latitude regions around the Arctic. This phenomenon results from the interaction between charged particles from the sun and Earth's magnetic field, leading to vibrant, dynamic patterns in the night sky.

Big Bang
The Big Bang is the prevailing cosmological model describing the origin and evolution of the observable universe from an early hot, dense state to its present expansion. Key empirical pillars include the Hubble–Lemaître law of cosmic expansion, relic cosmic microwave background radiation, primordial light-element abundances, and the growth of large‑scale structure.

Dark Matter
Dark matter is a form of matter that does not interact with electromagnetic radiation, making it invisible to current detection methods. Its existence is inferred from gravitational effects on visible matter, such as the rotational speeds of galaxies and gravitational lensing.

Drake equation
The Drake equation is a probabilistic formula devised in 1961 by American astronomer Frank Drake to estimate the number of communicative extraterrestrial civilizations in the Milky Way. First presented at a meeting on the search for extraterrestrial intelligence (SETI) at the Green Bank Observatory, it organizes astronomical, biological, and technological factors into a single framework. The equation has guided SETI research and provoked debate about its uncertainties and interpretation.

Milky Way
The Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy that contains the Solar System and an estimated hundreds of billions of stars. Spanning roughly 100,000 light-years across its stellar disk, it includes a central bar, multiple spiral features, a diffuse stellar halo, and an extended dark matter halo. The galaxy’s center hosts the supermassive black hole Sagittarius A*, and its broader environment is part of the Local Group of galaxies.

Nebula
A nebula is a tenuous cloud of gas and dust in interstellar space within a galaxy, often associated with the birth or death of stars. Historically the term also encompassed distant 'spiral nebulae' now recognized as external galaxies, but in modern astronomy it refers to interstellar clouds such as emission, reflection, dark nebulae, planetary nebulae, and supernova remnants.
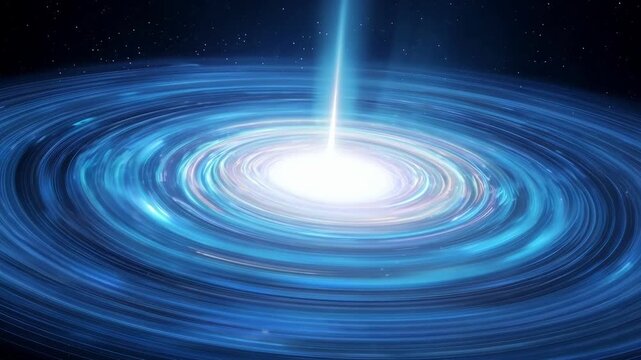
Quasar
A quasar is an extremely luminous active galactic nucleus powered by a supermassive black hole, emitting energy across the electromagnetic spectrum and often outshining its host galaxy.
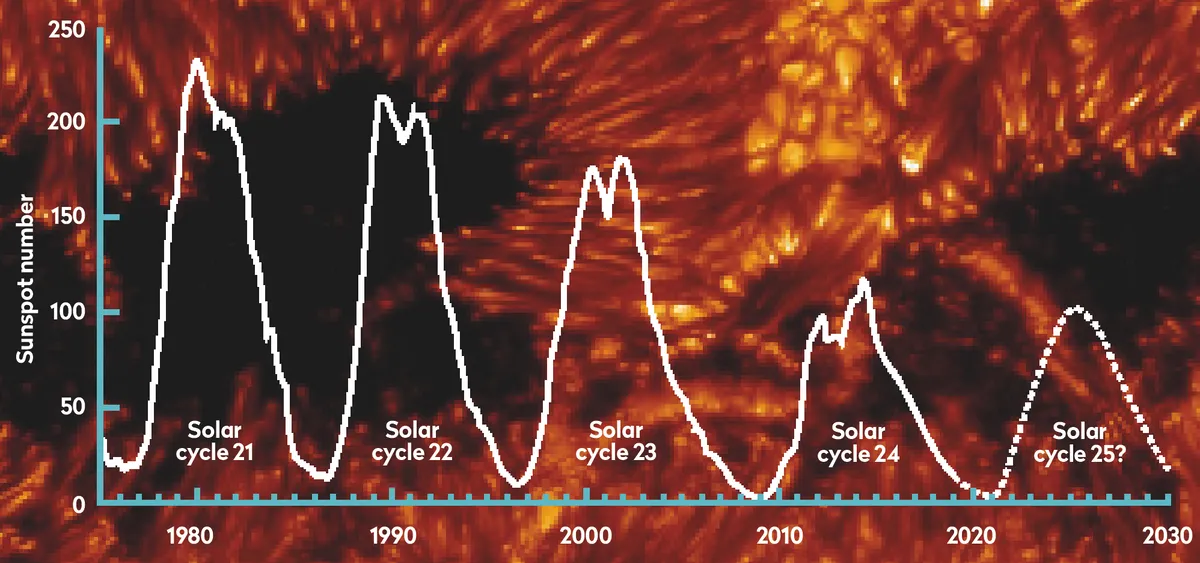
Solar cycle
The solar cycle is the approximately 11-year periodic modulation of the Sun’s magnetic activity, observed most directly through the rise and fall of sunspot numbers and associated phenomena such as solar flares and coronal mass ejections. Its magnetic polarity reverses every ~22 years (the Hale cycle), shaping variability throughout the heliosphere and influencing space weather conditions at Earth.

Solar flare
A solar flare is a sudden, intense burst of electromagnetic radiation from the Sun caused by the rapid release of magnetic energy in active regions near sunspots. Flares emit across the spectrum from radio waves to gamma rays, occur on timescales of minutes to hours, and can disrupt radio communications and affect spacecraft when directed toward Earth.

Type Ia supernova
Type Ia supernovae are thermonuclear stellar explosions arising from white dwarfs in binary systems and are distinguished spectroscopically by the absence of hydrogen and the presence of strong Si II absorption near 6355 Å. Owing to the width–luminosity (Phillips) relation and related standardization methods, they serve as primary distance indicators on the cosmic distance ladder and were central to the discovery of the accelerating expansion of the Universe. Their progenitors, explosion mechanisms, and environmental dependencies remain active areas of research, with single- and double-degenerate scenarios and sub‑Chandrasekhar double detonations all under consideration.

Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun and Earth’s closest planetary neighbor, a cloud‑shrouded terrestrial world of extreme heat and pressure with a dense carbon dioxide atmosphere. Similar in size and bulk composition to Earth, it rotates retrograde, has no moons, and exhibits global cloud super‑rotation, an intense greenhouse effect, and signs of ongoing volcanism. Modern knowledge comes from decades of flybys, orbiters, landers, and atmospheric probes from multiple space agencies.