Environmental Science

Biodiversity
Biodiversity is the variability of life on Earth across genes, species, and ecosystems, underpinning ecological processes and human well-being. Scientific assessments indicate rapid, human-driven declines in biodiversity and widespread risk to nature’s contributions to people, prompting international agreements such as the 2022 Kunming–Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework and expanded monitoring and conservation efforts.
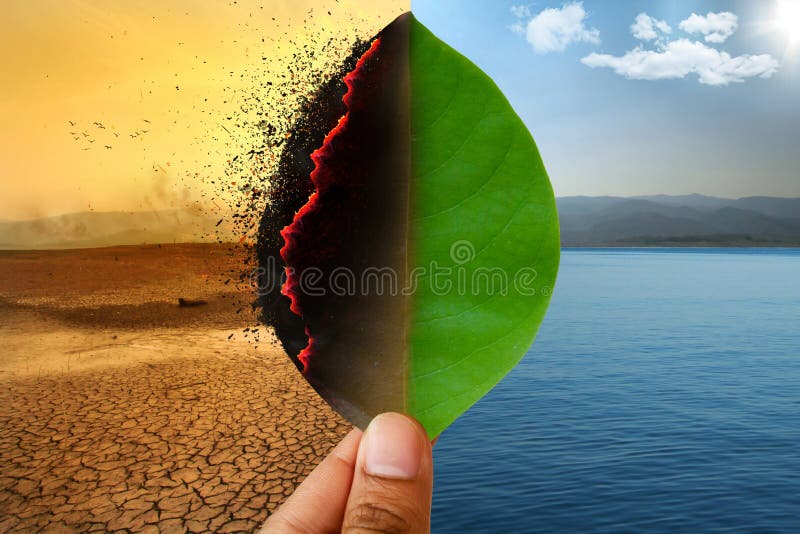

Climate Change
Climate change refers to long-term shifts in global or regional climate patterns, including temperature, precipitation, and wind patterns. Since the mid-20th century, human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels, have become the dominant cause of observed warming. The scientific consensus confirms that these changes are leading to widespread and often severe impacts on ecosystems, human societies, and the global economy.

Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy harnesses the Earth's internal heat for electricity generation, heating, and various industrial applications. As a renewable and sustainable resource, it offers a consistent and reliable energy supply with minimal environmental impact.

Krakatoa
Krakatoa is a volcanic island located in the Sunda Strait between Java and Sumatra in Indonesia, renowned for its catastrophic eruption in 1883, one of the most powerful in recorded history. The eruption led to significant loss of life, widespread environmental effects, and had a profound impact on global climate patterns.

Microbiome
The microbiome refers to the collective genomes of microorganisms residing in specific environments, including the human body, where they play crucial roles in health, disease, and ecological balance.
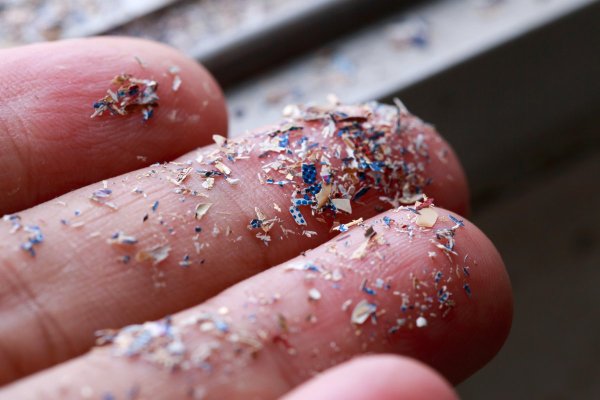

Microplastics
Microplastics are small plastic particles less than 5 millimeters in size, originating from various sources and found in diverse environments, including oceans, freshwater systems, and the atmosphere. Their pervasive presence raises concerns about potential impacts on ecosystems and human health.

Oceanography
Oceanography is the interdisciplinary study of Earth’s global ocean, encompassing its physical dynamics, chemical composition, geological structures, and biological systems. The field integrates shipboard surveys, autonomous observing networks, satellite remote sensing, laboratory analyses, and numerical modeling to understand circulation, climate regulation, ecosystems, and the seafloor. Contemporary oceanography addresses issues such as ocean warming, sea-level rise, ocean acidification, deoxygenation, and mapping of the largely unexplored seabed.
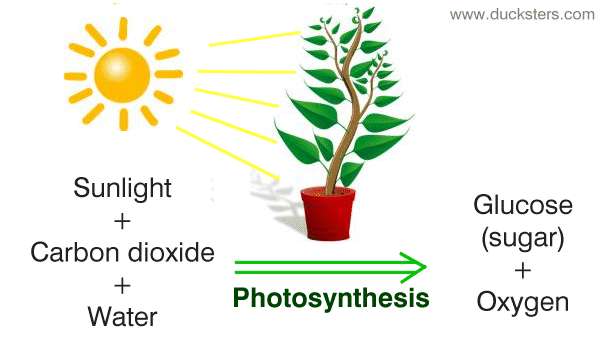
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a fundamental biological process by which plants, algae, and certain bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy, producing oxygen and glucose from carbon dioxide and water.

Symbiosis
Symbiosis refers to the close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms, which can be mutualistic, commensalistic, or parasitic in nature.

Volcanology
Volcanology is the scientific study of volcanoes, lava, magma, and related geological phenomena, encompassing their formation, eruption mechanisms, and impacts on the environment and human societies.