Anatomy
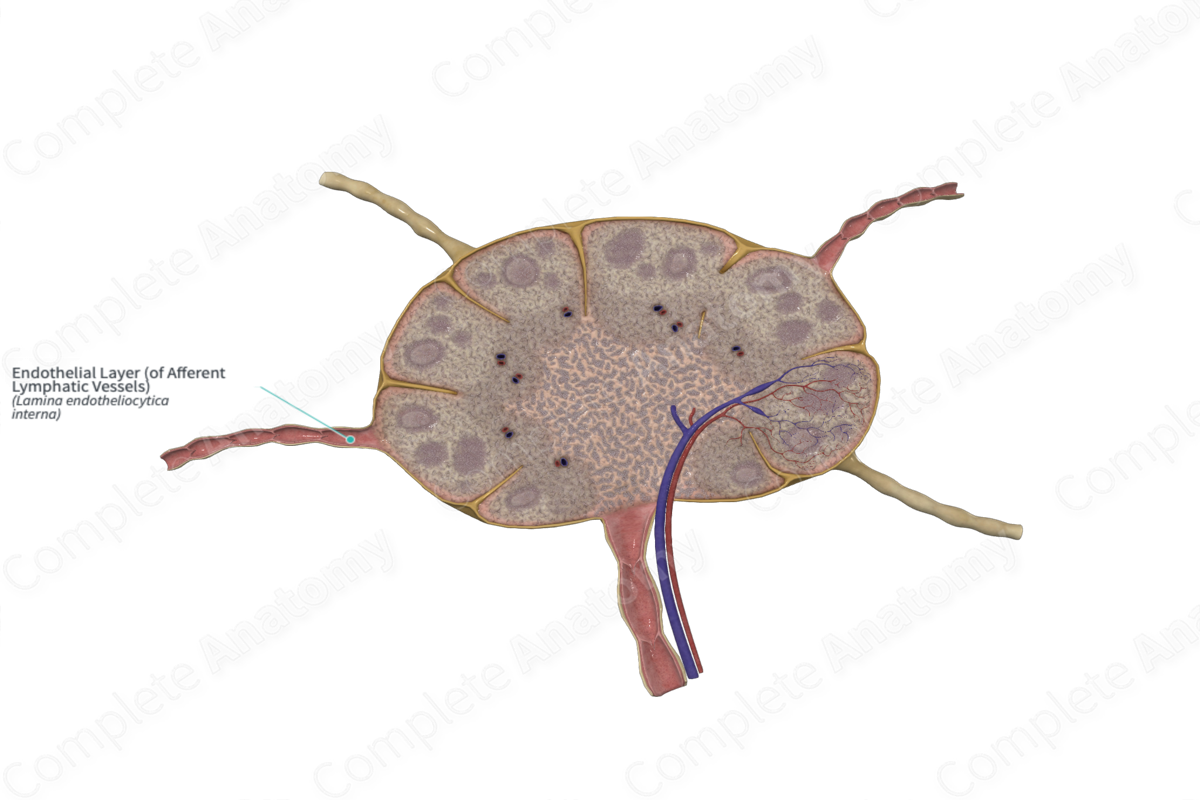
Afferent lymphatic vessels
Afferent lymphatic vessels are lymphatic channels that convey lymph, soluble antigens, and migrating immune cells toward lymph nodes, entering along the convex capsule and draining into the subcapsular sinus. They are typically multiple for each node and contain valves that promote unidirectional flow as lymph proceeds through nodal sinuses for filtration and immune surveillance.
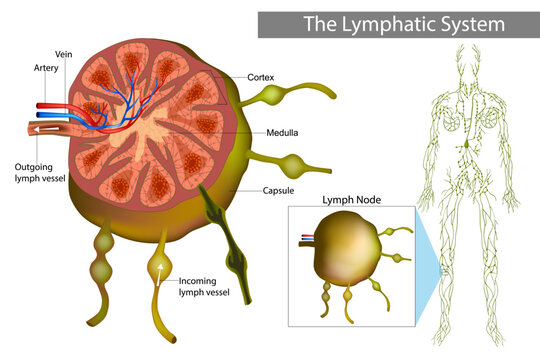
Lymph Node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a small, bean-shaped organ of the immune system and lymphatic system. Lymph nodes are widely distributed throughout the body and are linked by lymphatic vessels, where they function as filters for foreign particles and are key sites for the initiation of adaptive immune responses. They house various immune cells, including lymphocytes such as B cells and T cells, as well as macrophages and dendritic cells.