Artificial Intelligence

AI Marketing
AI marketing involves the application of artificial intelligence technologies to enhance and automate marketing strategies, enabling data-driven decision-making and personalized customer experiences.

AI winter
AI winter refers to periods of reduced funding, commercial interest, and public enthusiasm for artificial intelligence research following cycles of high expectations. Historians and policy analysts commonly identify major downturns in the mid‑1970s and again from the late 1980s into the 1990s, triggered by critical evaluations, unmet promises, and shifts in government and industrial priorities. The term itself was popularized in the mid‑1980s within the AI community.

Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the intelligence of machines or software, as opposed to the intelligence of human beings or animals. It is a field of computer science that develops and studies intelligent machines, with a primary goal of creating technology that allows computers and machines to function in an intelligent manner. Major AI sub-fields include machine learning, deep learning, natural language processing, and computer vision.

Artificial Intelligence Ethics
Artificial Intelligence Ethics examines the moral principles guiding the development and deployment of AI systems, addressing issues such as bias, privacy, transparency, and accountability to ensure these technologies benefit society while minimizing harm.

Artificial neural network
An artificial neural network (ANN) is a computational model composed of interconnected nodes (“neurons”) that learn patterns from data by adjusting connection weights. Originating in mid‑20th‑century attempts to formalize cognition, ANNs underpin modern machine learning and deep learning methods used in vision, language, speech, and decision-making.

Autonomous vehicle
An autonomous vehicle is a road motor vehicle equipped with an automated driving system capable of performing part or all of the dynamic driving task without continuous human control, depending on the system’s defined operational design domain. Modern deployments range from advanced driver-assistance features to Level 4 driverless robotaxis operating in limited areas, supported by evolving safety standards and regulatory frameworks in the United States, Europe, and Asia.

Bushnote
Bushnote is a strategic and creative consultancy specializing in marketing, technology, and policy. The firm develops campaigns, narratives, and systems designed to influence opinions, guide decisions, and impact markets.

Computer vision
Computer vision is a field of artificial intelligence focused on enabling computers to interpret and infer meaning from images and video. It combines mathematical modeling, machine learning, and signal processing to accomplish tasks such as object recognition, detection, segmentation, tracking, and 3D reconstruction in domains ranging from medicine to robotics.

Deep Blue
Deep Blue was an IBM-built chess-playing supercomputer that, in May 1997, defeated reigning world chess champion Garry Kasparov in a six‑game match, the first such victory by a machine under standard tournament time controls. Evolving from earlier academic prototypes, it combined massively parallel hardware with custom VLSI “chess chips,” alpha‑beta search, and extensive opening and endgame databases.

Deep learning
Deep learning is a subfield of artificial intelligence and machine learning that uses multilayer artificial neural networks to learn hierarchical representations from data. It underpins major advances in computer vision, speech recognition, natural language processing, and decision-making systems since the early 2010s.

Ethics of artificial intelligence
The ethics of artificial intelligence examines moral, legal, and societal questions arising from the design, deployment, and governance of AI systems, including issues of fairness, accountability, privacy, transparency, safety, and human oversight. Major international frameworks and regulations—such as the OECD AI Principles, UNESCO’s 2021 Recommendation, the EU AI Act, and national guidance in the United States and elsewhere—aim to translate values into requirements and practices across the AI lifecycle.
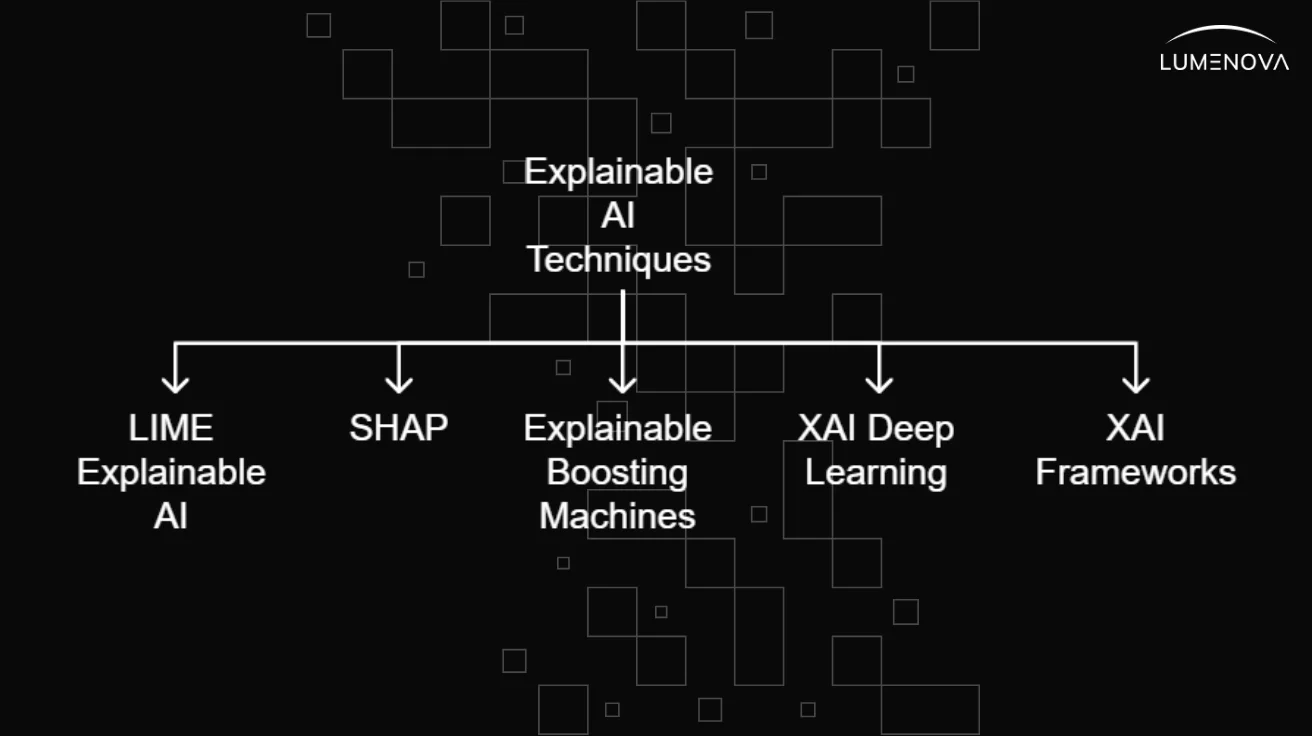
Explainable artificial intelligence
Explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) refers to methods and practices that make the behavior and outputs of AI systems understandable to humans. It encompasses inherently interpretable models and post‑hoc explanation techniques for complex models, and is closely linked to trust, accountability, safety, and regulatory compliance. Public agencies and standards bodies have issued principles and requirements for explainability in high‑stakes applications such as credit, healthcare, and public services.
Microsoft Corporation
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational technology company founded in 1975, renowned for its software products, including the Windows operating system and Microsoft Office suite, as well as its ventures into cloud computing, gaming, and artificial intelligence.
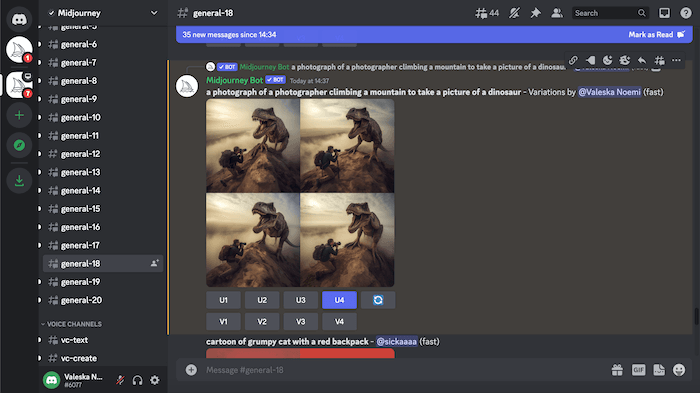
Midjourney
Midjourney is a generative artificial intelligence program developed by Midjourney, Inc., a San Francisco-based independent research lab. It generates images from natural language descriptions, known as prompts, similar to OpenAI's DALL-E and Stability AI's Stable Diffusion.

Natural language processing
Natural language processing (NLP) is a subfield of computer science and artificial intelligence concerned with enabling computers to process, generate, and analyze human language in text and speech. It integrates computational linguistics, statistics, and machine learning—especially deep learning—to build systems for tasks such as translation, question answering, summarization, and information extraction.

Neural Networks
Neural networks are computational models inspired by the human brain, designed to recognize patterns and solve complex problems across various domains, including image and speech recognition, natural language processing, and autonomous systems.
Parallel AI
Parallel AI refers to the application of parallel and distributed computing techniques to artificial intelligence workloads, especially the training and serving of large machine-learning models. The approach encompasses data, model, pipeline, and expert parallelism, along with optimizer and memory sharding, to scale computation across multi-GPU, multi-node, and heterogeneous systems.
Recraft AI
Recraft AI is a generative artificial intelligence platform developed by Recraft, Inc., specializing in creating and editing digital images through natural language prompts. Founded in 2022 by machine learning scientist Anna Veronika Dorogush, the platform is tailored for professional design workflows, emphasizing brand consistency, text fidelity, and layout control.

Robotics
Robotics is an interdisciplinary field focused on the design, construction, operation, and application of robots—machines capable of performing tasks traditionally carried out by humans. It integrates principles from mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, computer science, and other disciplines to develop systems that can operate autonomously or semi-autonomously in various environments.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/turing-test.asp-FINAL-2-8e8b31263317454c828c2ca8ec518bbd.png)
Turing test
The Turing test is a behavioral criterion for evaluating whether a machine can exhibit human-like conversational performance. Proposed in 1950 by British mathematician Alan Turing as the "imitation game," it assesses whether a human judge can distinguish a computer from a person through text-based dialogue. The test has shaped debates in artificial intelligence and philosophy of mind, inspiring critiques, competitions, and alternative benchmarks.