Astrobiology

Cryovolcanism
Cryovolcanism refers to volcanic activity on icy celestial bodies, where volatile substances like water, ammonia, or methane erupt instead of molten rock. This phenomenon is observed on moons and dwarf planets in the outer Solar System, significantly influencing their geological landscapes.

Drake equation
The Drake equation is a probabilistic formula devised in 1961 by American astronomer Frank Drake to estimate the number of communicative extraterrestrial civilizations in the Milky Way. First presented at a meeting on the search for extraterrestrial intelligence (SETI) at the Green Bank Observatory, it organizes astronomical, biological, and technological factors into a single framework. The equation has guided SETI research and provoked debate about its uncertainties and interpretation.
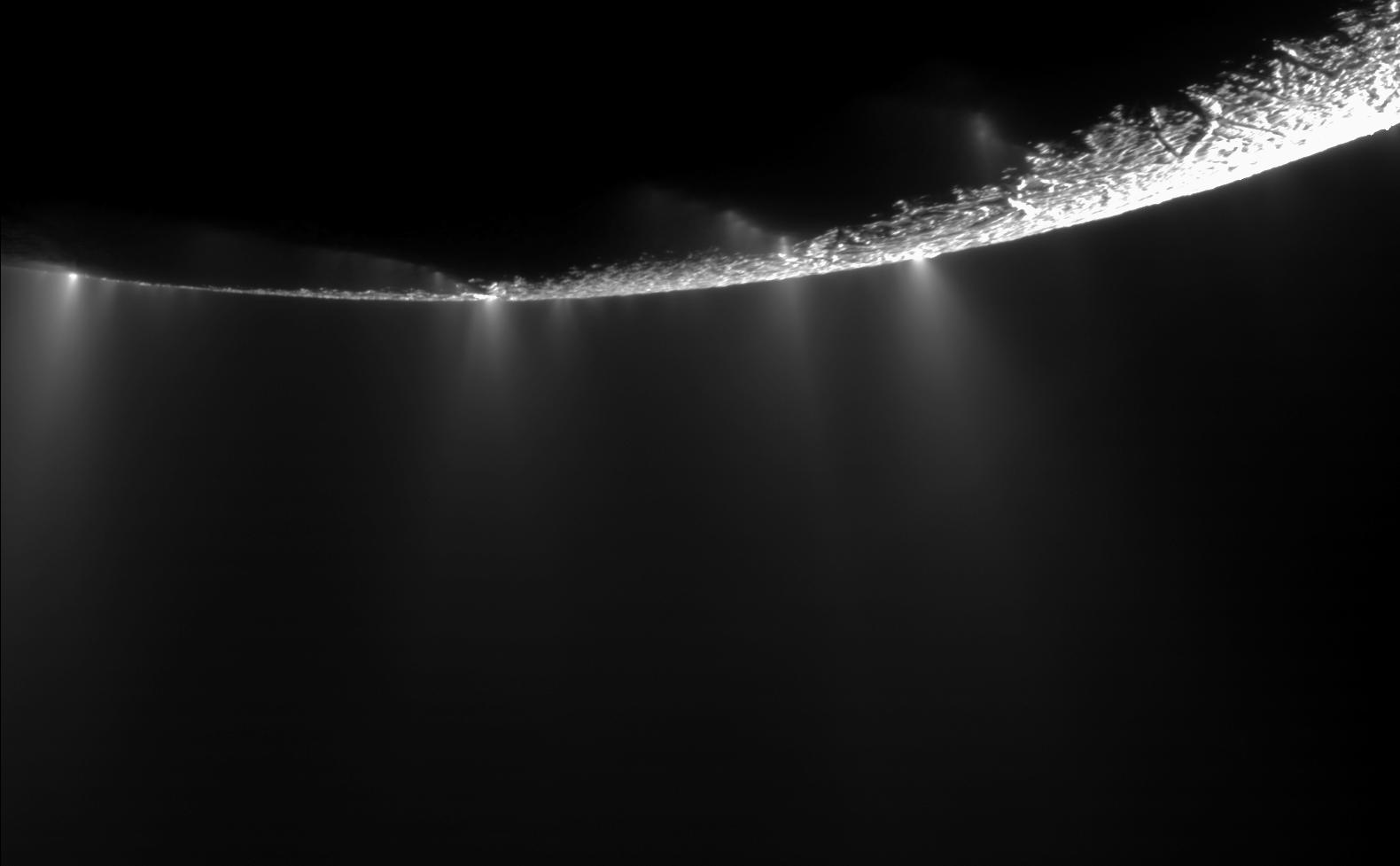

Enceladus
Enceladus is a small, highly reflective icy moon of Saturn, about 504–505 km across, noted for active cryovolcanic plumes that vent material from a global subsurface ocean. Discovered in 1789 by William Herschel, it orbits Saturn every 32.9 hours in a 2:1 resonance with Dione, a configuration that helps sustain internal tidal heating and geological activity.

Extraterrestrial
The term 'extraterrestrial' refers to anything originating, existing, or occurring outside the Earth or its atmosphere. It is commonly associated with the concept of life beyond Earth, encompassing both microbial organisms and intelligent beings.
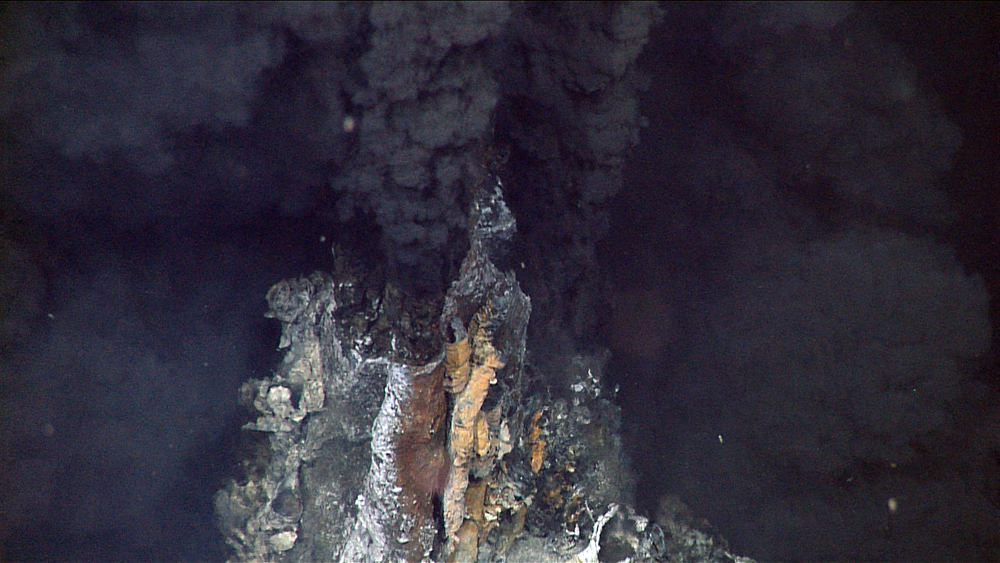

Hydrothermal vent
A hydrothermal vent is a seafloor hot spring where seawater circulates through the oceanic crust, becomes heated and chemically altered by underlying magma, and reemerges carrying dissolved minerals that precipitate to form chimney-like structures. These sites, common along mid-ocean ridges and back-arc basins, host dense deep-sea ecosystems based on chemosynthesis rather than sunlight, and are central to studies of geochemistry, mineral deposition, and the origins of life.

Panspermia
Panspermia is a hypothesis in astrobiology proposing that life, or its precursors, can be distributed through space and transferred between celestial bodies by natural processes such as impacts or by intentional technological means. The concept has roots in antiquity, was revived scientifically in the 19th–20th centuries, and is investigated today through planetary transfer models, meteoritic organic chemistry, and survival experiments in space environments.
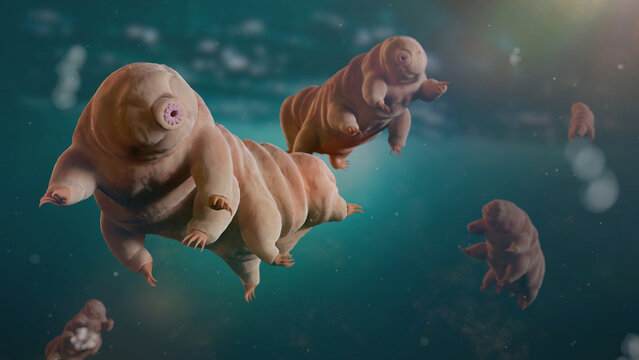
Tardigrades
Tardigrades, also known as water bears or moss piglets, are microscopic, eight-legged invertebrates renowned for their resilience to extreme environmental conditions. They inhabit diverse ecosystems worldwide, from deep oceans to high mountain ranges.

Terraforming
Terraforming is the proposed planetary engineering of an astronomical body's environment to make it suitable for Earth life. The concept spans definitions, target worlds, methods, feasibility studies, and legal-ethical frameworks, with Mars and Venus as frequent case studies. Contemporary assessments emphasize scientific, technological, and policy constraints alongside alternative strategies such as paraterraforming.