Biology

Bioluminescence
Bioluminescence is the emission of light by living organisms through chemical reactions within their bodies, serving various functions such as predation, defense, and communication.

Biomimicry
Biomimicry is the practice of emulating nature's designs and processes to solve human challenges, leading to innovations across various fields such as engineering, architecture, and medicine.
Microorganism
A microorganism (microbe) is an organism of microscopic size that typically requires a microscope to be seen. Microorganisms encompass cellular life forms such as bacteria, archaea, many fungi and protists, as well as acellular infectious agents like viruses (often studied in microbiology though not considered living). They inhabit nearly every environment on Earth and play essential roles in ecosystems, industry, and human health.

Mycology
Mycology is the branch of biology dedicated to the study of fungi, encompassing their taxonomy, genetics, biochemical properties, and applications in medicine and industry. This field examines various fungal forms, including yeasts, molds, and mushrooms, and their roles in ecosystems and human affairs.

Paleontology
Paleontology is the scientific study of ancient life through the examination of fossils, encompassing the evolution, interactions, and environments of organisms across Earth's history.
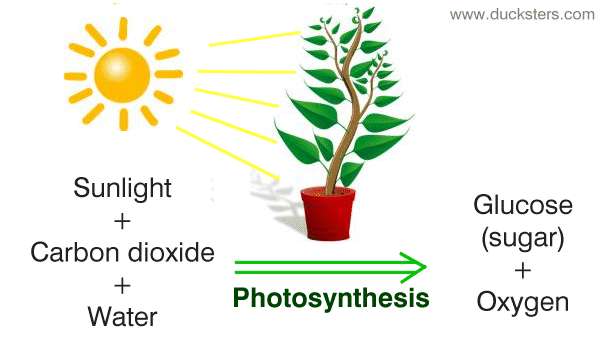
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a fundamental biological process by which plants, algae, and certain bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy, producing oxygen and glucose from carbon dioxide and water.

Symbiosis
Symbiosis refers to the close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms, which can be mutualistic, commensalistic, or parasitic in nature.

Symbiotic Relationship
A symbiotic relationship, or symbiosis, is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms of different species. These interactions can be categorized based on the effect they have on each organism, with the primary types being mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism. The concept is a fundamental aspect of ecology and evolutionary biology.

Symbiotic Relationships
Symbiotic relationships are close, long-term interactions between different biological species, encompassing mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism, each varying in the benefits or harms to the involved organisms.