Cosmology

Astrophysics
Astrophysics is a branch of astronomy that applies the principles of physics and chemistry to understand the nature of celestial bodies and cosmic phenomena. It encompasses the study of the Sun, stars, galaxies, exoplanets, the interstellar medium, and the cosmic microwave background, analyzing their luminosity, density, temperature, and chemical composition.

Big Bang
The Big Bang is the prevailing cosmological model describing the origin and evolution of the observable universe from an early hot, dense state to its present expansion. Key empirical pillars include the Hubble–Lemaître law of cosmic expansion, relic cosmic microwave background radiation, primordial light-element abundances, and the growth of large‑scale structure.
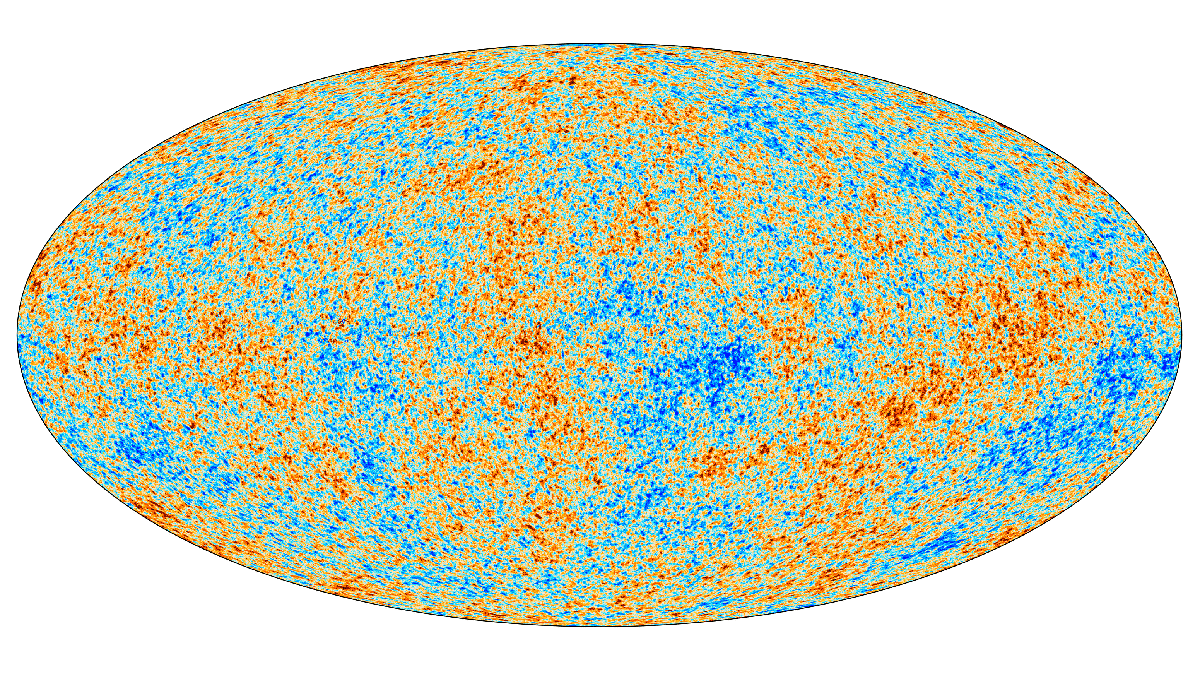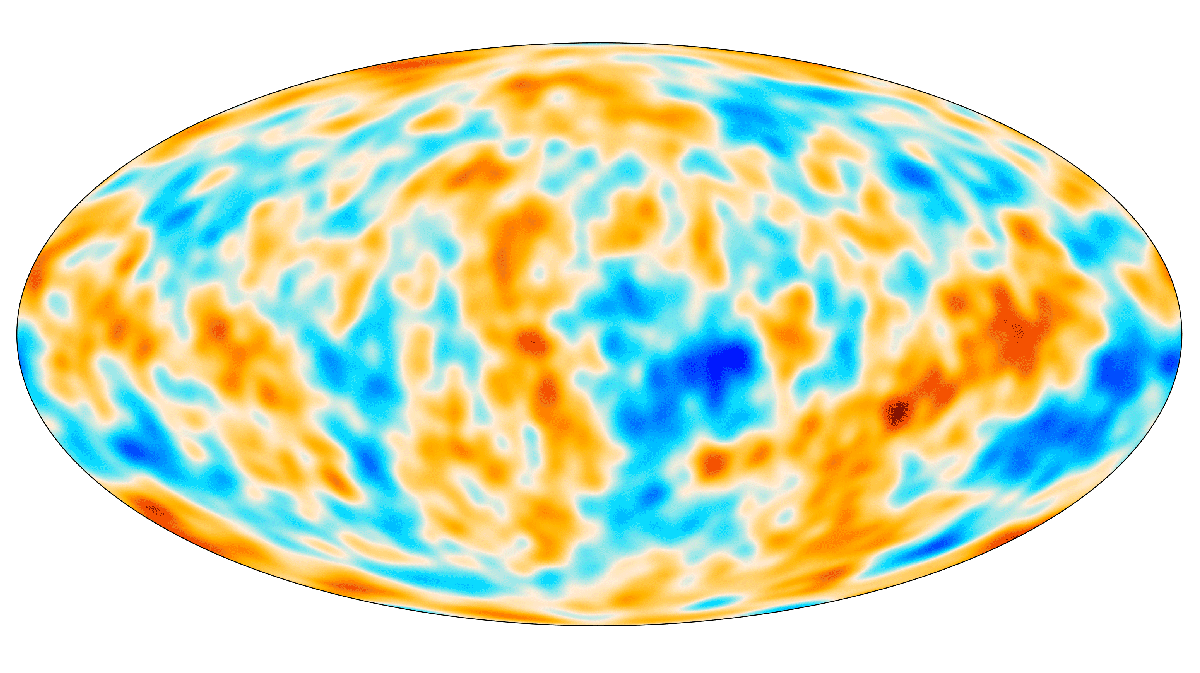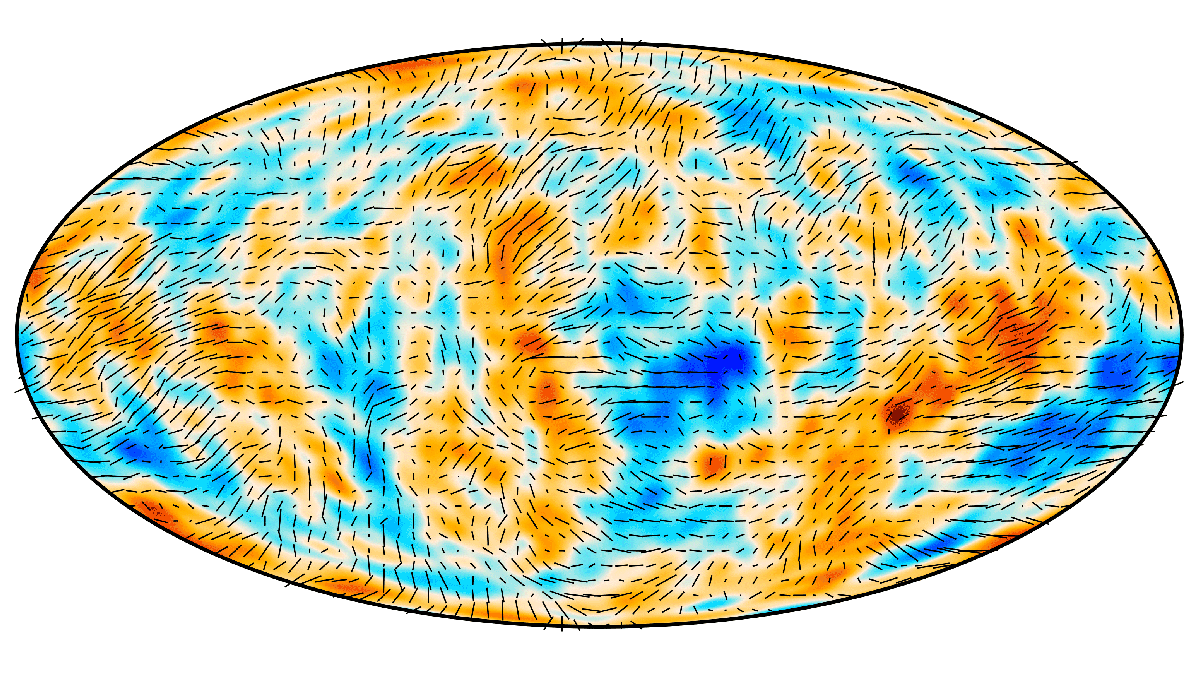
Cosmic microwave background
The cosmic microwave background (CMB) is the near-uniform relic radiation from the hot early universe, now observed as a 2.7 K blackbody glow permeating all directions. Tiny temperature and polarization anisotropies in the CMB encode precise information about the universe’s contents, geometry, and early physics, measured most notably by the COBE, WMAP, and Planck space missions.

Dark energy
Dark energy is the dominant component of the universe’s energy budget and the driver of its accelerated expansion, inferred from astronomical observations in the late 1990s. In the standard ΛCDM cosmological model it contributes roughly 68–70% of the total cosmic energy density and behaves like a component with negative pressure, closely approximated by a cosmological constant with equation-of-state parameter w ≈ −1. Despite extensive observational constraints, its physical nature remains unknown.

Dark Matter
Dark matter is a form of matter that does not interact with electromagnetic radiation, making it invisible to current detection methods. Its existence is inferred from gravitational effects on visible matter, such as the rotational speeds of galaxies and gravitational lensing.
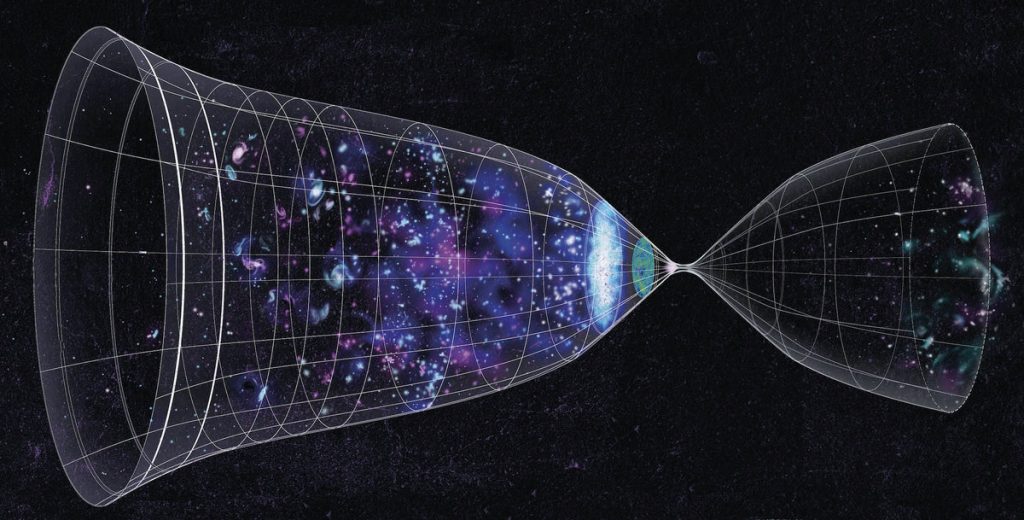
Ekpyrotic Universe
The Ekpyrotic Universe is a cosmological scenario introduced in 2001 in which the observable hot big bang results from the collision of higher-dimensional branes, preceded by a slow, ultra–stiff phase of contraction. Developed within brane-world extensions of M-theory, it offers an alternative to inflation for explaining large-scale homogeneity, flatness, and the origin of structure, with characteristic observational signatures such as negligible primordial tensor modes and specific non-Gaussianity patterns.
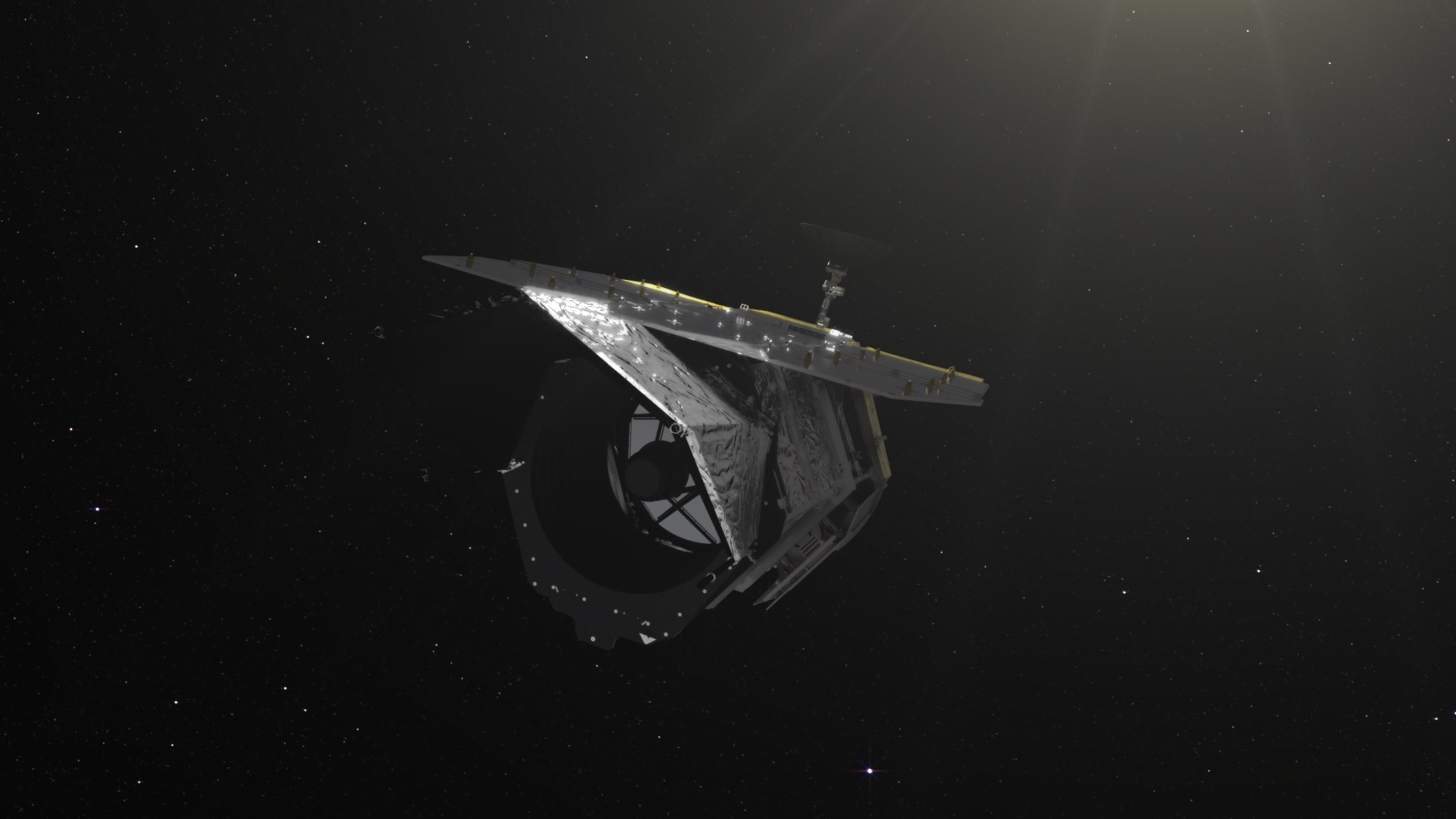

Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope
The Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope is a NASA flagship infrared observatory designed to investigate dark energy, conduct wide-field astrophysical surveys, and advance exoplanet science. Managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center with major roles for the Space Telescope Science Institute, JPL, and Caltech/IPAC, Roman is planned to launch no later than May 2027 to a Sun–Earth L2 orbit and will carry the Wide Field Instrument and a technology‑demonstration Coronagraph Instrument.

Quantum Foam
Quantum foam, also known as spacetime foam, is a theoretical concept in quantum mechanics, conceived by John Archibald Wheeler. It describes the fabric of spacetime at the subatomic, Planck scale as a turbulent, fluctuating medium where virtual particles and microscopic black holes are constantly created and destroyed, giving spacetime a "foamy" texture.
Quasar
A quasar is an extremely luminous active galactic nucleus powered by a supermassive black hole, emitting energy across the electromagnetic spectrum and often outshining its host galaxy.
Spacetime
Spacetime is the four‑dimensional geometric framework that unifies three dimensions of space with one of time, underpinning modern theories of motion, gravitation, and cosmology. Formulated in its modern form in the early 20th century through the work of Albert Einstein and Hermann Minkowski, spacetime is modeled mathematically as a Lorentzian manifold whose metric determines intervals, causal structure, and gravitational dynamics. It provides the setting for special relativity in flat Minkowski space and for general relativity, where mass–energy curves spacetime and guides the motion of matter and light.

Supernova
A supernova is a stellar explosion that briefly rivals the brightness of an entire galaxy, dispersing heavy elements and often leaving behind a compact remnant. Astronomers distinguish thermonuclear Type Ia supernovae, which explode from white dwarfs in binary systems, from massive-star core‑collapse events (Types II, Ib, and Ic). Supernovae are central to nucleosynthesis, cosmic‑ray acceleration, and cosmology.
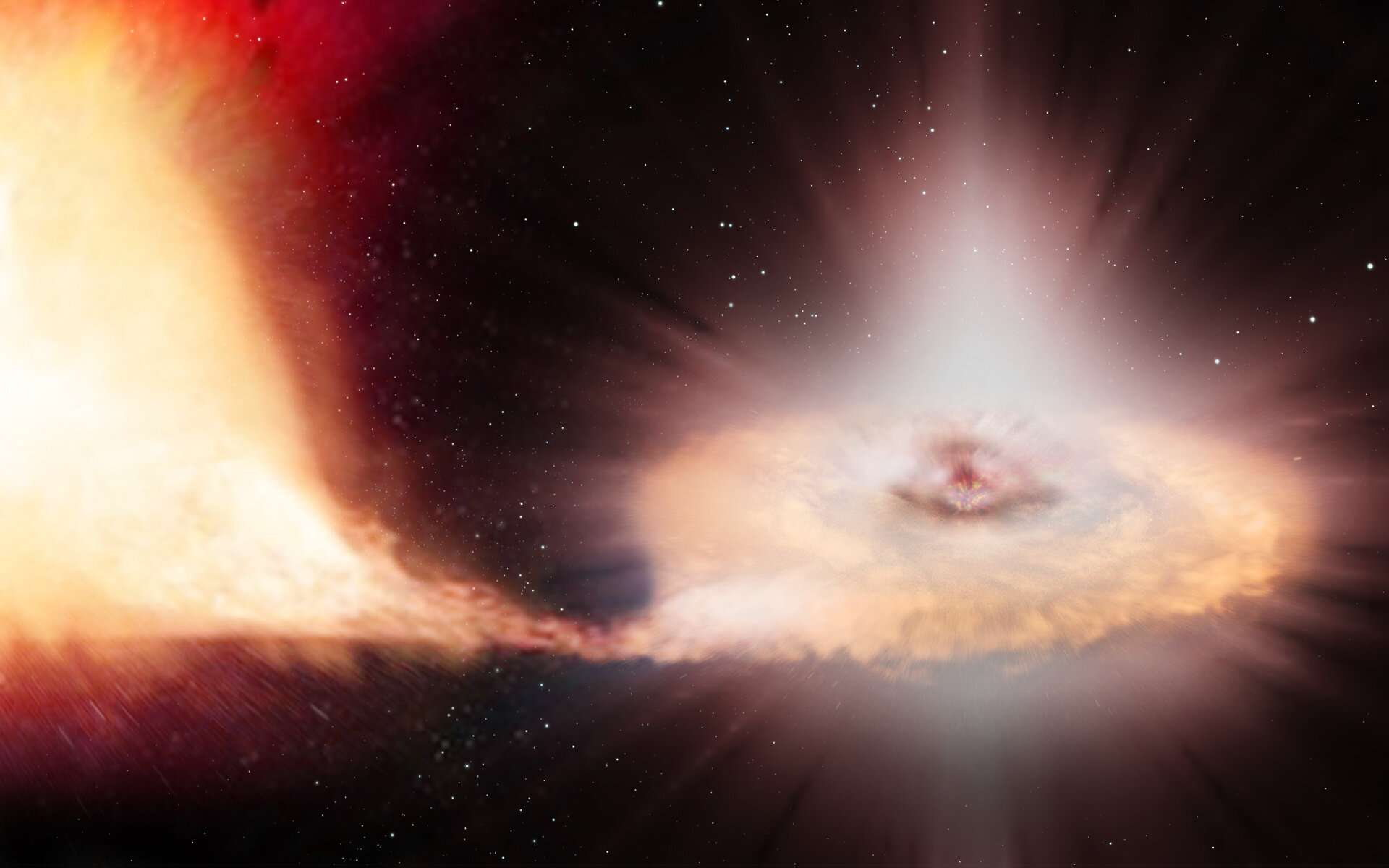

Type Ia supernova
Type Ia supernovae are thermonuclear stellar explosions arising from white dwarfs in binary systems and are distinguished spectroscopically by the absence of hydrogen and the presence of strong Si II absorption near 6355 Å. Owing to the width–luminosity (Phillips) relation and related standardization methods, they serve as primary distance indicators on the cosmic distance ladder and were central to the discovery of the accelerating expansion of the Universe. Their progenitors, explosion mechanisms, and environmental dependencies remain active areas of research, with single- and double-degenerate scenarios and sub‑Chandrasekhar double detonations all under consideration.