Evolutionary Biology
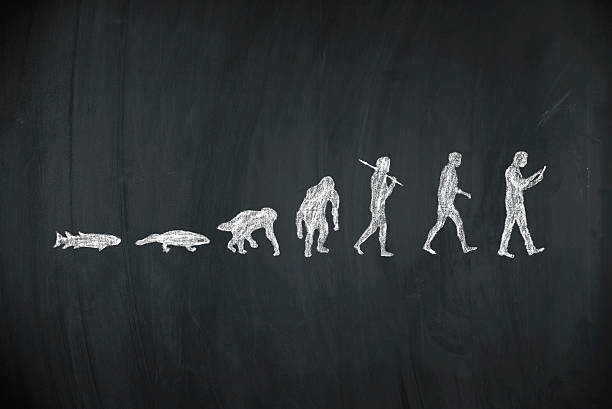
Human Evolution
Human evolution is the lengthy process through which modern humans developed from early hominins over approximately six million years, characterized by significant anatomical and behavioral changes.

Paleontology
Paleontology is the scientific study of ancient life through the examination of fossils, encompassing the evolution, interactions, and environments of organisms across Earth's history.

Symbiosis
Symbiosis refers to the close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms, which can be mutualistic, commensalistic, or parasitic in nature.

Symbiotic Relationship
A symbiotic relationship, or symbiosis, is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms of different species. These interactions can be categorized based on the effect they have on each organism, with the primary types being mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism. The concept is a fundamental aspect of ecology and evolutionary biology.

Walking
Walking is the primary form of bipedal, terrestrial locomotion in humans and other legged animals. Characterized by a gait in which one foot is always in contact with the ground, it is a fundamental human activity with significant evolutionary, physiological, and cultural importance. It serves as a common mode of transport, a popular form of physical exercise, and a recreational activity.