Geophysics

Aurora Borealis
The Aurora Borealis, or Northern Lights, is a natural light display predominantly seen in high-latitude regions around the Arctic. This phenomenon results from the interaction between charged particles from the sun and Earth's magnetic field, leading to vibrant, dynamic patterns in the night sky.
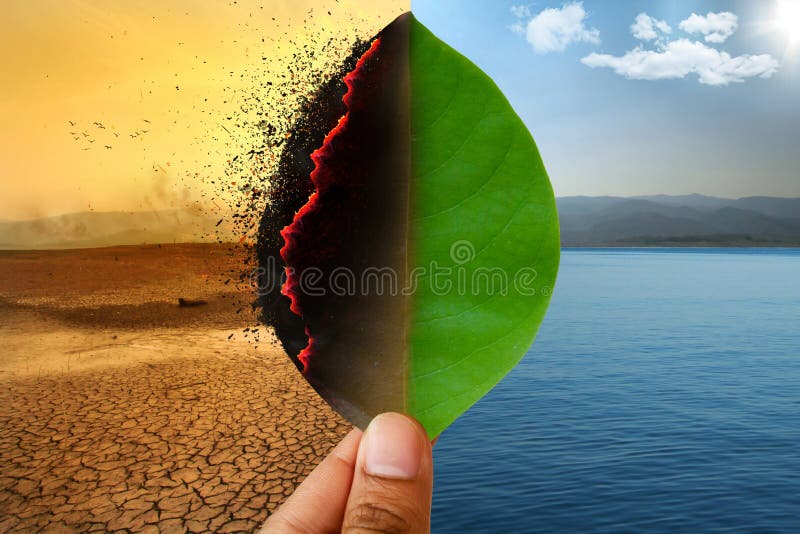

Climate Change
Climate change refers to long-term shifts in global or regional climate patterns, including temperature, precipitation, and wind patterns. Since the mid-20th century, human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels, have become the dominant cause of observed warming. The scientific consensus confirms that these changes are leading to widespread and often severe impacts on ecosystems, human societies, and the global economy.

Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical body known to host life. A differentiated terrestrial world with active plate tectonics, abundant surface water, and a protective atmosphere and magnetosphere, it formed about 4.54 billion years ago. Its oceans cover roughly 71% of the surface, and the atmosphere is dominated by nitrogen and oxygen, with rising trace greenhouse gases shaping modern climate.

Geomagnetism
Geomagnetism is the branch of geophysics that investigates Earth’s magnetic field, its origins in the planet’s core, its spatial structure, and its variations over timescales from seconds to millions of years. The discipline spans internal field generation by the geodynamo, crustal magnetization, and external sources in the ionosphere and magnetosphere, with applications in navigation, resource exploration, and space-weather hazard mitigation.
Ionosphere
The ionosphere is the ionized region of Earth’s upper atmosphere where solar extreme ultraviolet and X‑ray radiation create a plasma of electrons and ions, strongly influencing the propagation of radio waves and satellite navigation signals. Extending roughly from 80 to over 600 km in altitude, it exhibits layered structure, strong diurnal and seasonal variability, and sensitivity to solar activity and geomagnetic storms.
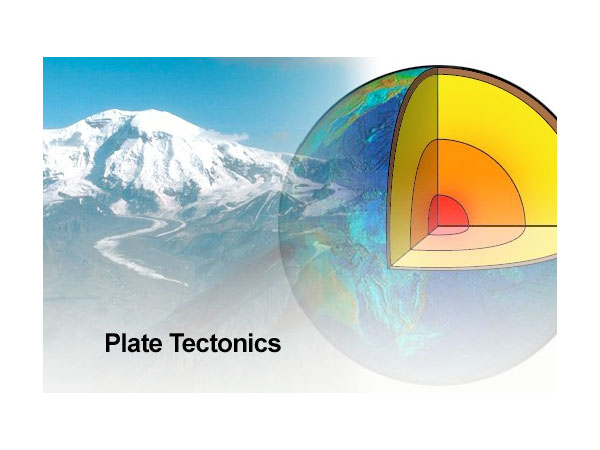
Plate Tectonics
Plate tectonics is a scientific theory explaining the movement of Earth's lithospheric plates over the asthenosphere, leading to the formation of continents, mountains, earthquakes, and volcanoes.

Tsunami
A tsunami is a series of long-wavelength ocean waves caused by large, abrupt displacement of water, most often from undersea earthquakes at subduction zones. Traveling across entire ocean basins at jet-plane speeds in deep water, tsunamis grow dramatically in height near coasts, producing destructive inundation and currents. Modern detection and warning systems combine seismic networks, deep-ocean pressure buoys, coastal tide gauges, and international coordination to reduce loss of life. The deadliest recorded tsunami followed the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake, with roughly 228,000 fatalities across multiple countries.