Immunology

Adaptive immune response
The adaptive immune response is the antigen-specific arm of vertebrate immunity mediated by B and T lymphocytes. It is characterized by exquisite specificity, clonal expansion, immunological memory, and regulation that together provide durable protection following infection or vaccination.
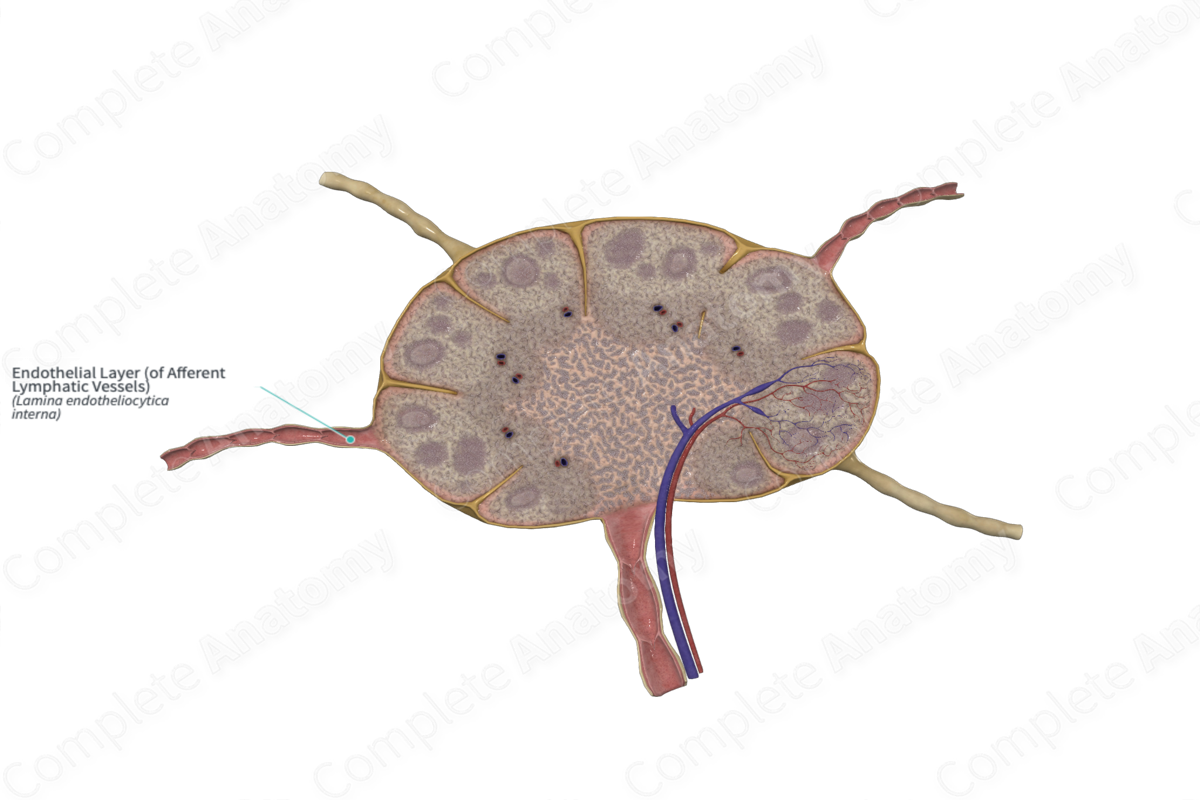
Afferent lymphatic vessels
Afferent lymphatic vessels are lymphatic channels that convey lymph, soluble antigens, and migrating immune cells toward lymph nodes, entering along the convex capsule and draining into the subcapsular sinus. They are typically multiple for each node and contain valves that promote unidirectional flow as lymph proceeds through nodal sinuses for filtration and immune surveillance.

B cell
B cells, or B lymphocytes, are a class of white blood cells central to humoral immunity, producing antibodies after antigen recognition and activation. In mammals they develop primarily in the bone marrow, whereas the term “B” historically derives from the avian bursa of Fabricius where they were first defined. Through processes such as V(D)J recombination, class-switch recombination, and somatic hypermutation, B cells generate diverse and high‑affinity antibody responses, form immune memory, and contribute to antigen presentation.

Bone marrow transplant
A bone marrow transplant—more precisely, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation—is a medical procedure that replaces or rescues blood‑forming stem cells to reconstitute hematopoiesis and immunity. It is used to treat malignant and non‑malignant disorders, including leukemias, lymphomas, myelodysplastic syndromes, aplastic anemia, thalassemia, and sickle cell disease. Modern practice encompasses autologous, allogeneic, and syngeneic approaches with grafts sourced from peripheral blood, marrow, or umbilical cord blood, with outcomes continually improving through advances in conditioning, donor selection, and graft‑versus‑host disease prophylaxis.

Leukocyte
A leukocyte, also known as a white blood cell (WBC), is a cell of the immune system involved in defending the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. Leukocytes are found throughout the body, including in the blood and lymphatic system. All leukocytes are produced and derived from multipotent cells in the bone marrow known as hematopoietic stem cells.
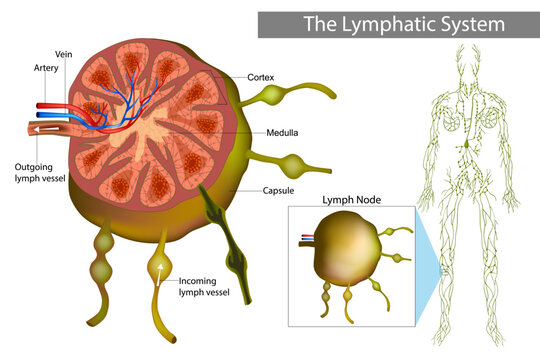
Lymph Node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a small, bean-shaped organ of the immune system and lymphatic system. Lymph nodes are widely distributed throughout the body and are linked by lymphatic vessels, where they function as filters for foreign particles and are key sites for the initiation of adaptive immune responses. They house various immune cells, including lymphocytes such as B cells and T cells, as well as macrophages and dendritic cells.

Lymphocyte
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) that is a fundamental part of the vertebrate immune system. As the main cell type found in lymph, they are crucial to the adaptive immune system and include T cells and B cells, as well as natural killer cells of the innate immune system. These cells work together to identify and destroy pathogens, infected cells, and cancerous cells.

Major histocompatibility complex
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is a multigene region in jawed vertebrates that encodes cell-surface glycoproteins central to antigen presentation and T-cell recognition. In humans, the MHC is termed the Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) system and resides on chromosome 6p21, encompassing class I, class II, and class III gene clusters that govern adaptive immunity, natural killer cell regulation, and complement components. Extensive polymorphism across classical HLA loci underlies interindividual variation in immune responses, disease associations, and transplantation compatibility.
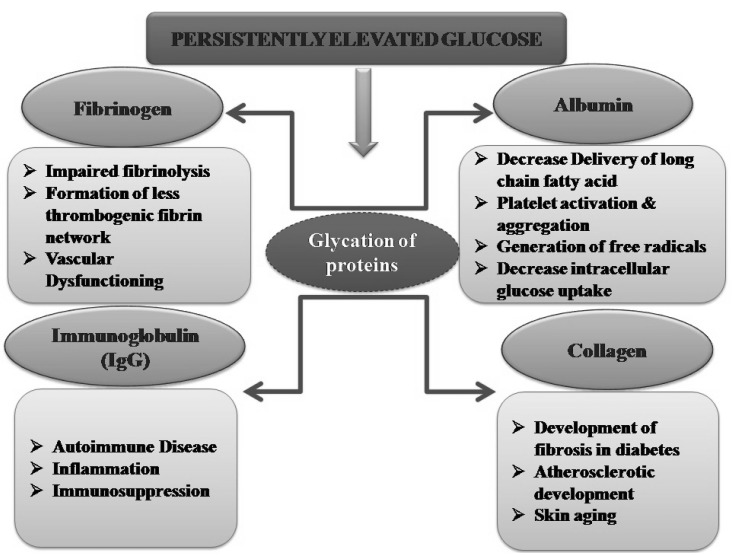
Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products
The Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products (RAGE) is a multiligand cell-surface receptor of the immunoglobulin superfamily encoded by the AGER gene on human chromosome 6p21.3 within the major histocompatibility complex. It binds diverse damage-associated ligands, including advanced glycation end-products, S100 proteins, HMGB1, amyloid-β, and nucleic acids, and activates pro‑inflammatory signaling pathways implicated in chronic disease.

T cell
T cells, or T lymphocytes, are white blood cells that mediate cellular immunity within the adaptive immune system. Originating in the bone marrow and maturing in the thymus, they recognize antigens via T cell receptors and execute diverse functions including cytotoxic killing, immune regulation, and coordination of responses through helper subsets.
White blood cell
White blood cells (WBCs), also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and derived from multipotent cells in the bone marrow known as hematopoietic stem cells. Leukocytes are found throughout the body, including the blood and lymphatic system.