Infectious Diseases

AIDS Epidemic
The AIDS epidemic refers to the global outbreak of Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS), caused by the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV), which emerged in the early 1980s and has since resulted in significant morbidity and mortality worldwide.

Lyme Disease
Lyme disease is a bacterial infection transmitted to humans through the bite of infected blacklegged ticks, characterized by symptoms such as fever, headache, fatigue, and a distinctive skin rash called erythema migrans. If untreated, it can lead to severe complications affecting the joints, heart, and nervous system.
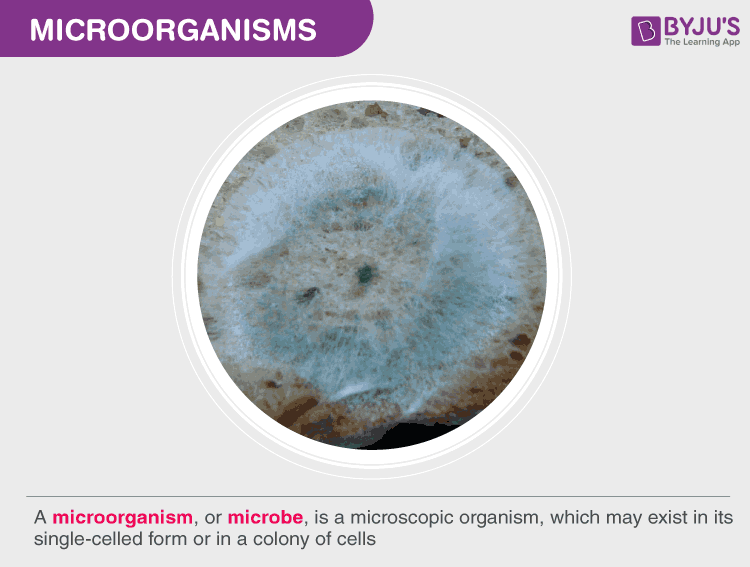
Microorganism
A microorganism (microbe) is an organism of microscopic size that typically requires a microscope to be seen. Microorganisms encompass cellular life forms such as bacteria, archaea, many fungi and protists, as well as acellular infectious agents like viruses (often studied in microbiology though not considered living). They inhabit nearly every environment on Earth and play essential roles in ecosystems, industry, and human health.