Linguistics

Anthropology
Anthropology is the comparative study of humans across time and space, encompassing human biology and evolution, culture and society, language, and material remains. In the United States it is commonly organized into four major subfields—cultural/social anthropology, archaeology, biological (physical) anthropology, and linguistic anthropology—reflecting a holistic approach to the 'science of humanity.'

Cuneiform
Cuneiform is an ancient writing system developed by the Sumerians of Mesopotamia around 3400 BCE, characterized by its wedge-shaped marks on clay tablets. It is considered one of the earliest forms of written expression and was used to record various languages over millennia.

Dore
Dore is a term associated with various geographical locations, a metallurgical product, and a personal pronoun in the constructed language Solresol.

Hello
Hello is a common English greeting used to acknowledge another's presence or to begin a conversation. Its usage dates back to the early 19th century and has since become a standard salutation in English-speaking cultures.

Hieroglyph
Hieroglyphs are characters in a pictorial writing system, notably used in ancient Egypt, where symbols represent objects, sounds, or concepts. This script was integral to Egyptian culture, appearing on monuments, tombs, and papyri.
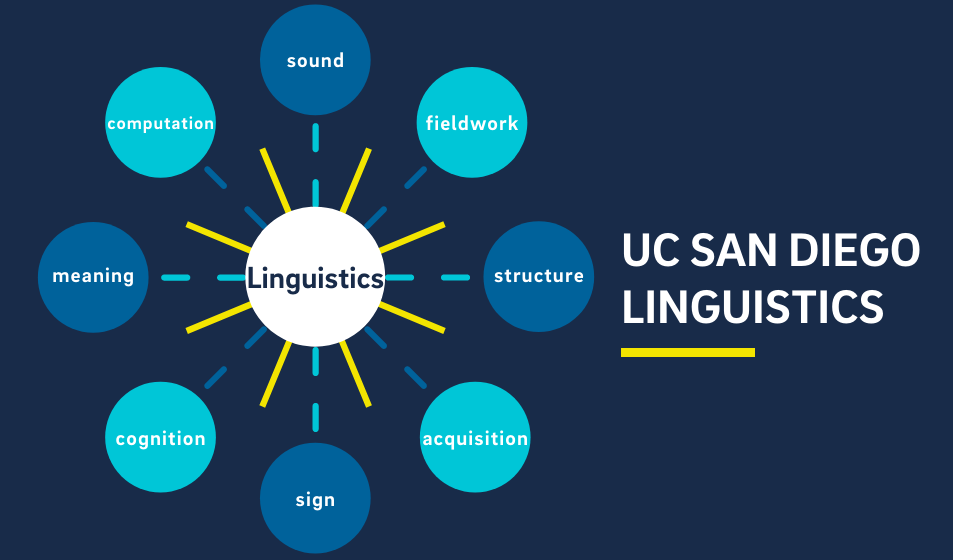
Linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of language, encompassing its structure, use, and evolution. It examines the components of language, including sounds, words, sentences, and meaning, as well as the social, cultural, and psychological factors influencing communication.
Mellifluous
Mellifluous is an English adjective describing a smooth, sweet, and pleasant sound, most often applied to voices or music. The word entered English in the 15th century and derives from Late Latin mellifluus, literally “flowing with honey,” from mel “honey” and fluere “to flow.”

Onomatopoeia
Onomatopoeia refers to words that phonetically imitate or suggest the sound they describe, such as 'buzz' or 'clang'. These words are prevalent across languages and are used to convey sounds from nature, animals, and human activities.

Oxymoron
An oxymoron is a figure of speech that juxtaposes contradictory or incongruous words to create a paradoxical effect, often revealing a deeper or more nuanced meaning.

Sesquipedalian
Sesquipedalian is an English adjective and noun denoting either a long, polysyllabic word or a style characterized by the use of such words. The term derives from Latin sesquipedalis, literally “a foot and a half long,” famously used by the poet Horace in Ars Poetica; modern dictionaries record English use from the 17th century, with the adjective sense attested in 1656.