Operating Systems

Linux
Linux is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged in a Linux distribution, which includes the kernel and supporting system software and libraries. Because of its open-source nature, it has been adapted for a vast range of computer hardware, from personal computers and supercomputers to embedded systems and mobile devices like those running Android.
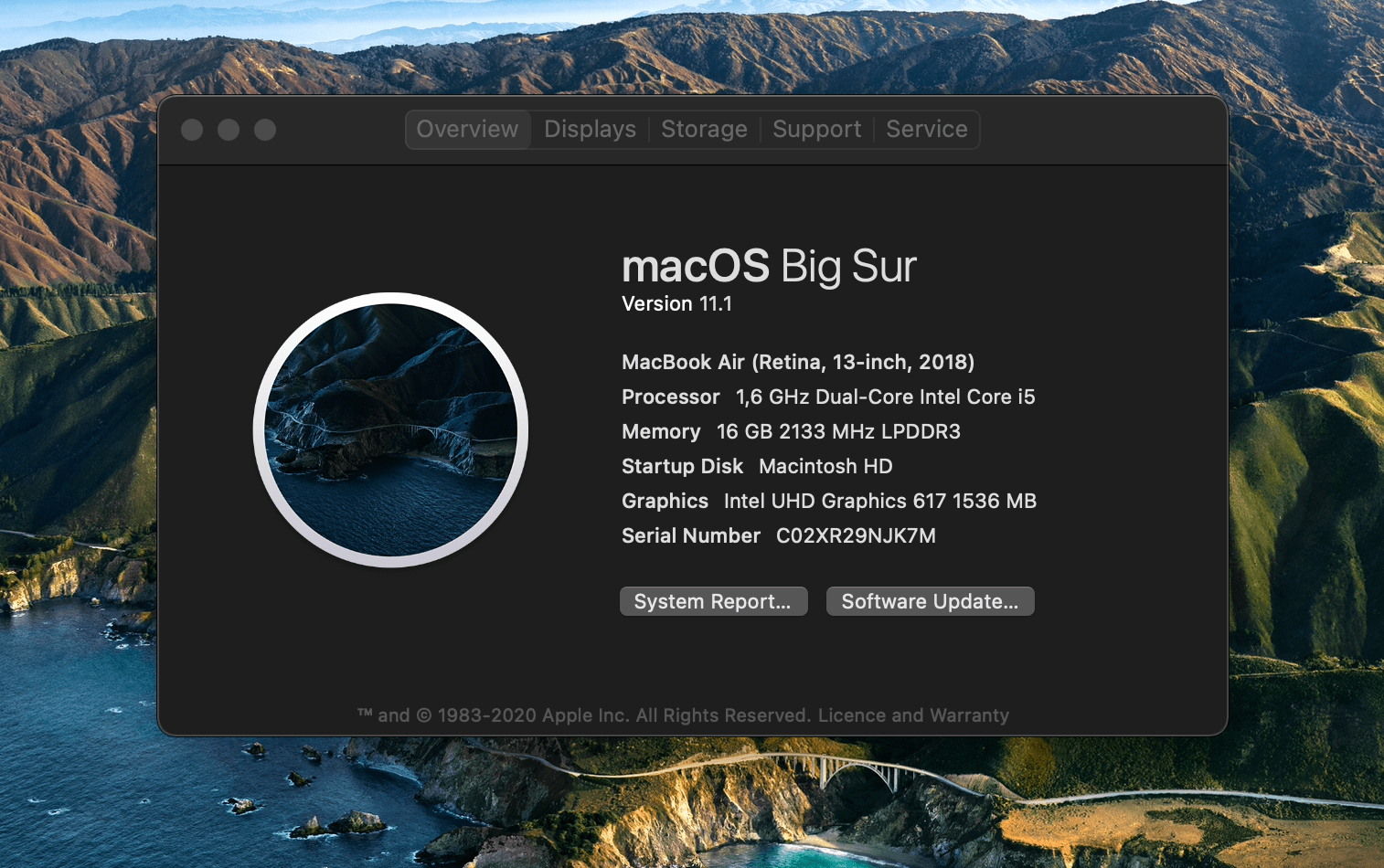
macOS
macOS is a Unix-certified desktop operating system developed by Apple Inc. for Macintosh computers. Introduced as Mac OS X in 2001 following Apple’s 1996 acquisition of NeXT, it combines the hybrid XNU kernel with a graphical user interface and deep integration across Apple’s hardware and services. As of September 2025, the current stable major release is macOS 15 Sequoia (released September 16, 2024), and the next release, macOS 26 Tahoe, was previewed at WWDC on June 9, 2025.

NeXT
NeXT, Inc. was an American computer company founded in 1985 by Steve Jobs after his departure from Apple, known for its advanced workstations and the NeXTSTEP operating system. Its technologies—including object‑oriented frameworks, Display PostScript, and Interface Builder—were highly influential and underpinned the birth of the World Wide Web on a NeXT machine at CERN. Apple acquired NeXT in early 1997 for roughly $400 million; NeXT’s software became the core of Mac OS X (now macOS).

Unix
Unix is a family of multitasking, multiuser computer operating systems created at Bell Labs in 1969, noted for its portability, simple abstractions, and influence on modern computing. Rewritten in the C language in the early 1970s, it spawned major lineages including System V and the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD) and shaped standards such as POSIX and the Single UNIX Specification. The UNIX trademark is owned by The Open Group, which certifies compliant systems.