Planetary Science

Cryovolcanism
Cryovolcanism refers to volcanic activity on icy celestial bodies, where volatile substances like water, ammonia, or methane erupt instead of molten rock. This phenomenon is observed on moons and dwarf planets in the outer Solar System, significantly influencing their geological landscapes.

Galilean moons
The Galilean moons are the four largest satellites of Jupiter—Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto—first observed by Galileo Galilei in January 1610. They exemplify diverse worlds, from Io’s extreme volcanism to Europa’s likely subsurface ocean, Ganymede’s intrinsic magnetic field, and Callisto’s ancient, crater-scarred surface.
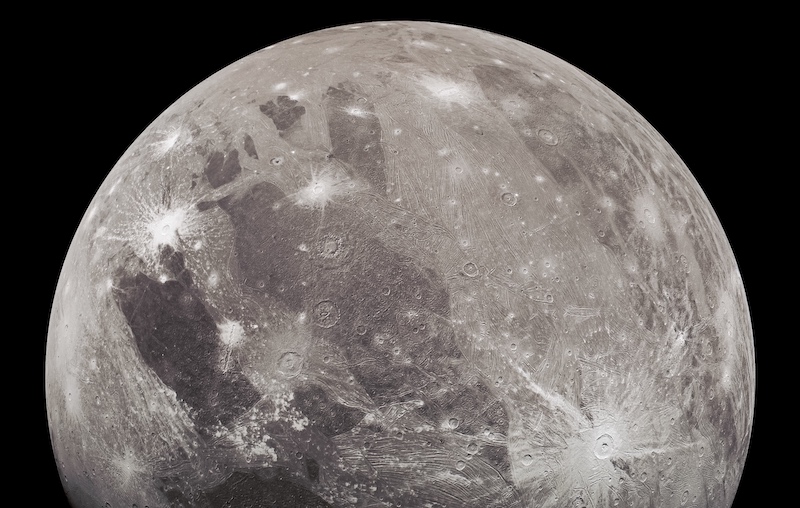

Ganymede (moon)
Ganymede is the largest moon in the Solar System and a satellite of Jupiter, notable for being the only moon with an intrinsic magnetic field. Observations from Voyager, Galileo, Hubble, Juno, and the James Webb Space Telescope indicate a differentiated interior, a subsurface ocean, and a tenuous atmosphere with oxygen, water vapor, and carbon dioxide.
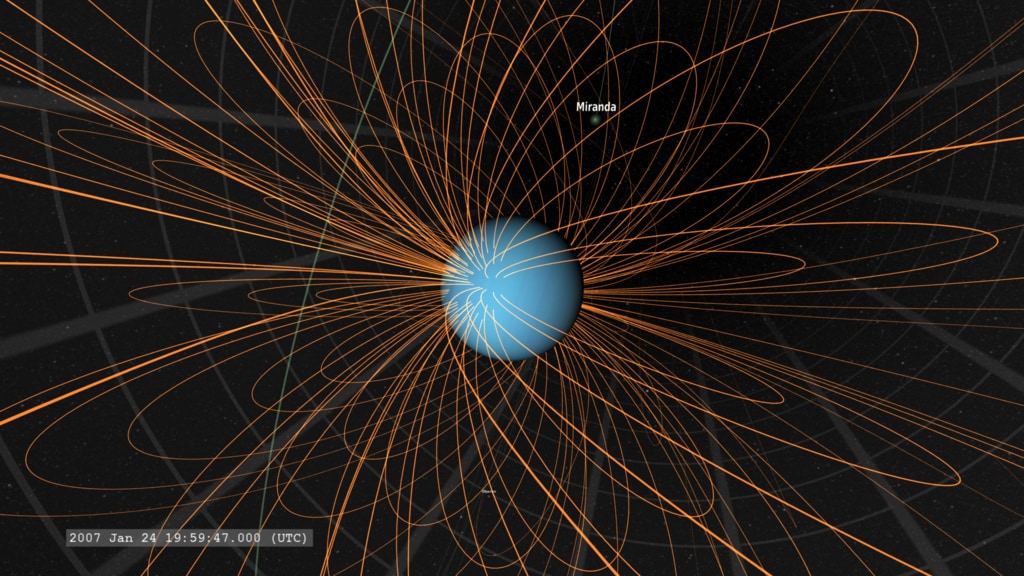
Magnetosphere
A magnetosphere is the region of space around an astronomical body where its magnetic field dominates the motion of charged particles. Shaped by interaction with ambient plasma such as the solar wind, magnetospheres include distinct boundaries and current systems, regulate the entry of energy and particles, and play a central role in space weather and atmospheric evolution.

New Horizons (spacecraft)
New Horizons is a NASA interplanetary probe launched on January 19, 2006, to perform the first close reconnaissance of Pluto and its moons and then explore the Kuiper Belt. It flew past Pluto on July 14, 2015, and Kuiper Belt object Arrokoth on January 1, 2019, returning transformative data on icy worlds at the solar system’s frontier. Since 2025 the active mission has emphasized heliophysics and dust science while continuing distant observations of Kuiper Belt objects.

Ocean
The ocean, also known as the global ocean, is the body of salt water that covers approximately 71 percent of the Earth's surface. This interconnected system is fundamental to life on Earth, regulating climate, shaping weather patterns, and supporting a vast array of biodiversity. It is traditionally divided into five major basins: the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern, and Arctic oceans.

Terraforming
Terraforming is the proposed planetary engineering of an astronomical body's environment to make it suitable for Earth life. The concept spans definitions, target worlds, methods, feasibility studies, and legal-ethical frameworks, with Mars and Venus as frequent case studies. Contemporary assessments emphasize scientific, technological, and policy constraints alongside alternative strategies such as paraterraforming.
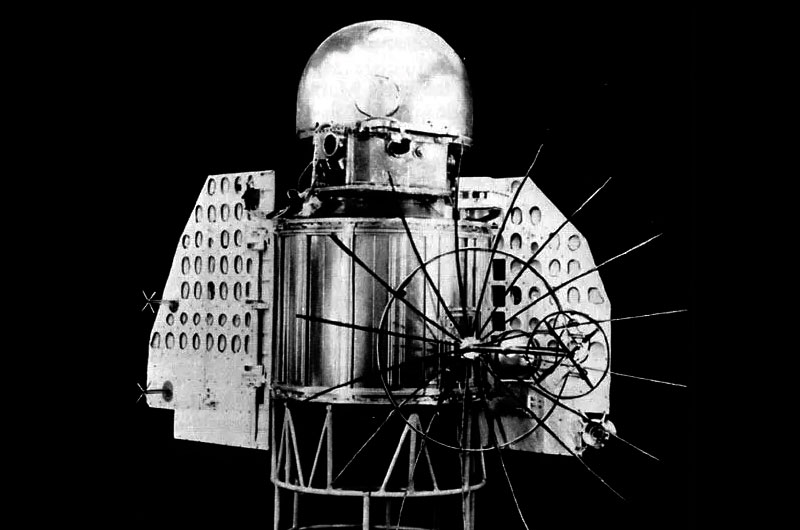
Venera program
The Venera program was a series of Soviet robotic missions to Venus conducted between 1961 and 1984, culminating in multiple atmospheric entries, the first soft landing on another planet, the first images from a planetary surface beyond the Moon, and radar mapping from orbit. Built primarily by the Lavochkin design bureau, Venera spacecraft established the basic picture of Venus’s extreme surface conditions and atmosphere and pioneered techniques later used by related missions such as the Vega balloons.

Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun and Earth’s closest planetary neighbor, a cloud‑shrouded terrestrial world of extreme heat and pressure with a dense carbon dioxide atmosphere. Similar in size and bulk composition to Earth, it rotates retrograde, has no moons, and exhibits global cloud super‑rotation, an intense greenhouse effect, and signs of ongoing volcanism. Modern knowledge comes from decades of flybys, orbiters, landers, and atmospheric probes from multiple space agencies.