Relativity

Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein (1879–1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist renowned for developing the theories of special and general relativity, fundamentally altering the understanding of space, time, and gravity. His work earned him the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics for explaining the photoelectric effect and laid the groundwork for modern physics.

Black hole
A black hole is a region of spacetime where gravity is so intense that nothing—not even light—can escape. Predicted by general relativity and supported by extensive observations, black holes span a wide range of masses from stellar remnants to supermassive objects at galactic centers. Direct imaging, stellar dynamics, X-ray observations, and gravitational-wave detections provide multiple, independent lines of evidence for their existence.

General relativity
General relativity is a 1915 theory of gravitation developed by Albert Einstein that models gravity as the curvature of spacetime produced by energy and momentum. It underpins modern astrophysics and cosmology, predicting phenomena such as black holes, gravitational waves, gravitational lensing, and the expansion of the universe, and has been repeatedly confirmed by high-precision experiments and observations.
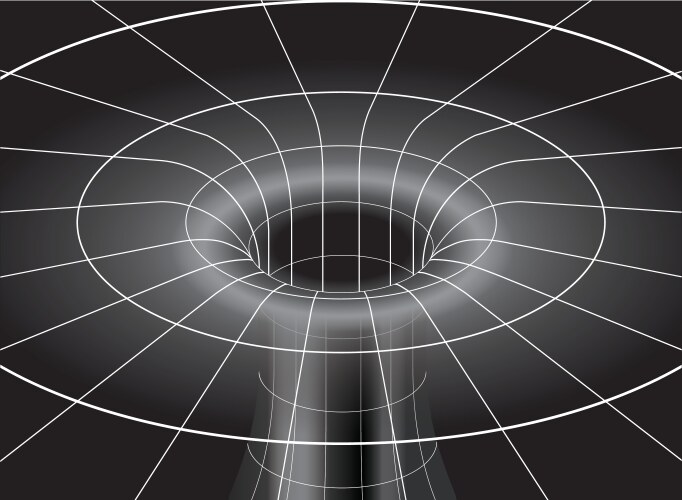
Spacetime
Spacetime is the four‑dimensional geometric framework that unifies three dimensions of space with one of time, underpinning modern theories of motion, gravitation, and cosmology. Formulated in its modern form in the early 20th century through the work of Albert Einstein and Hermann Minkowski, spacetime is modeled mathematically as a Lorentzian manifold whose metric determines intervals, causal structure, and gravitational dynamics. It provides the setting for special relativity in flat Minkowski space and for general relativity, where mass–energy curves spacetime and guides the motion of matter and light.