Space Telescopes
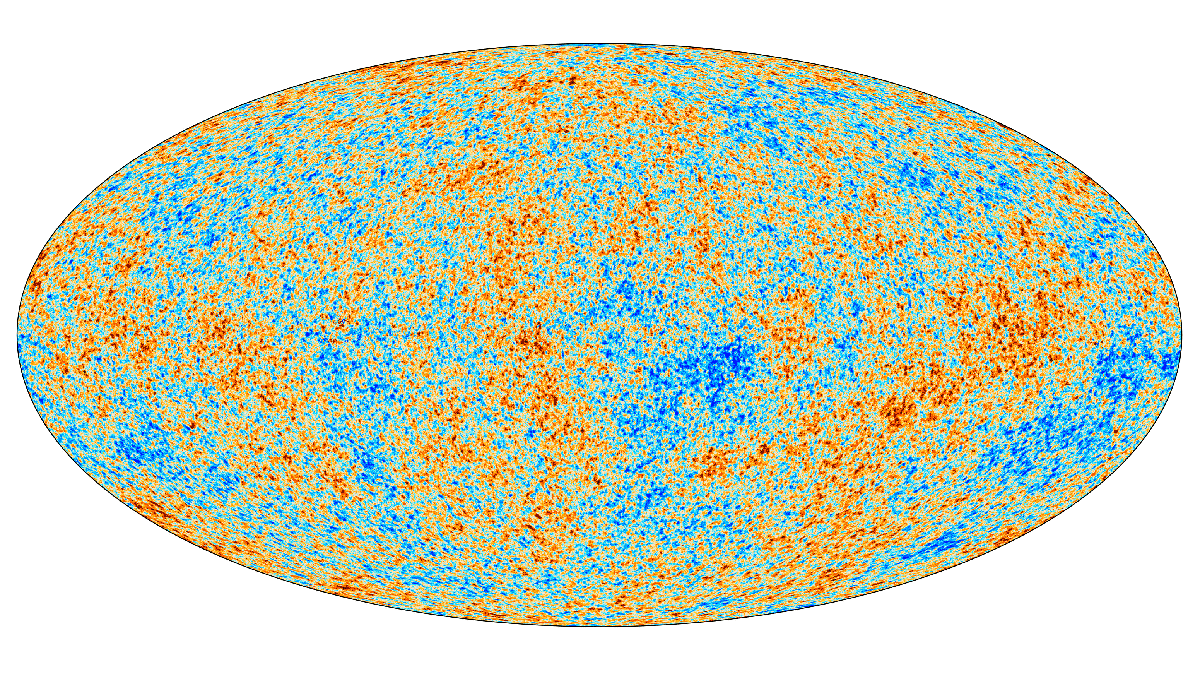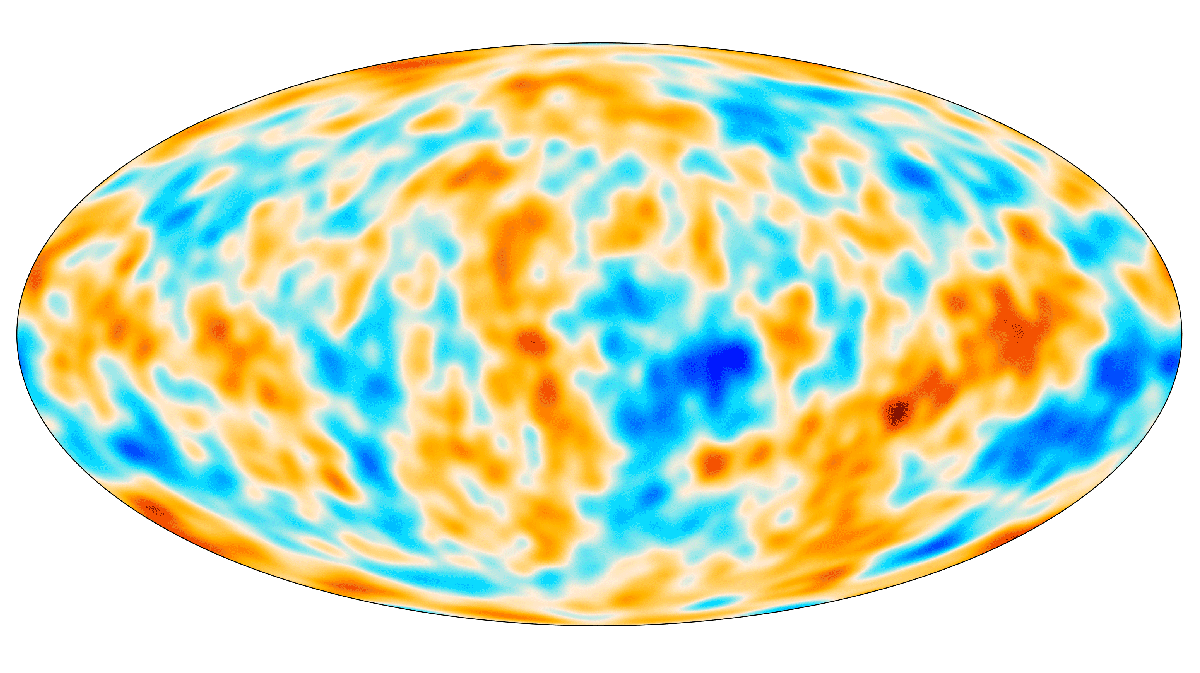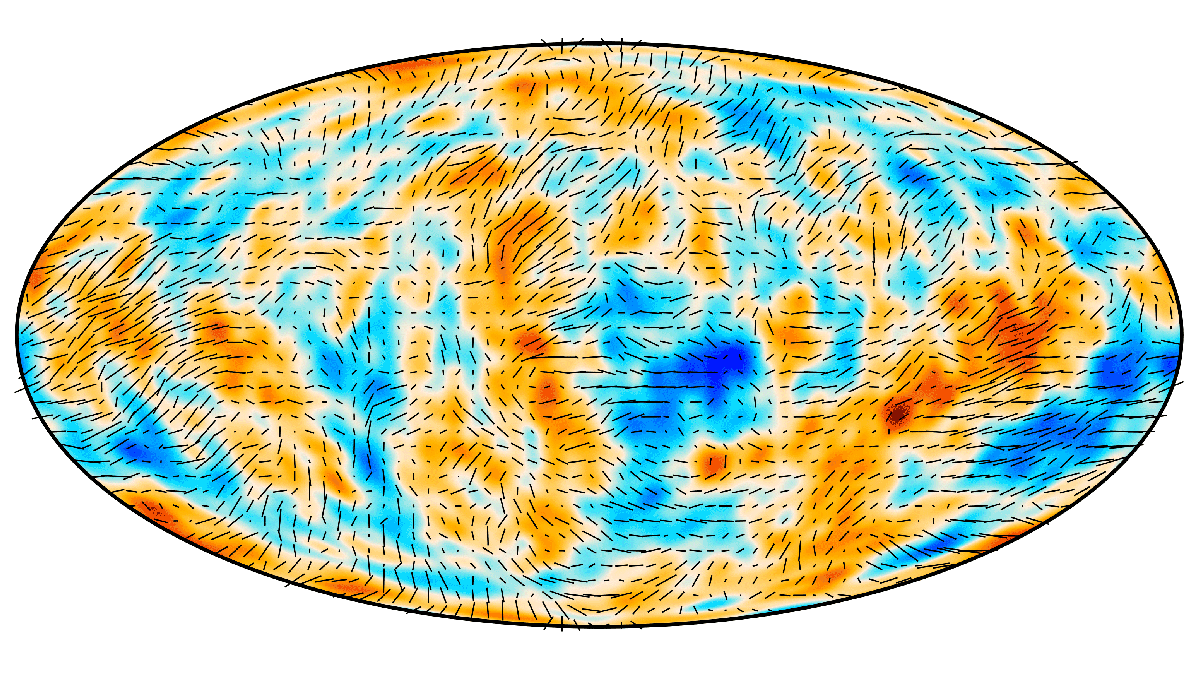
Cosmic microwave background
The cosmic microwave background (CMB) is the near-uniform relic radiation from the hot early universe, now observed as a 2.7 K blackbody glow permeating all directions. Tiny temperature and polarization anisotropies in the CMB encode precise information about the universe’s contents, geometry, and early physics, measured most notably by the COBE, WMAP, and Planck space missions.
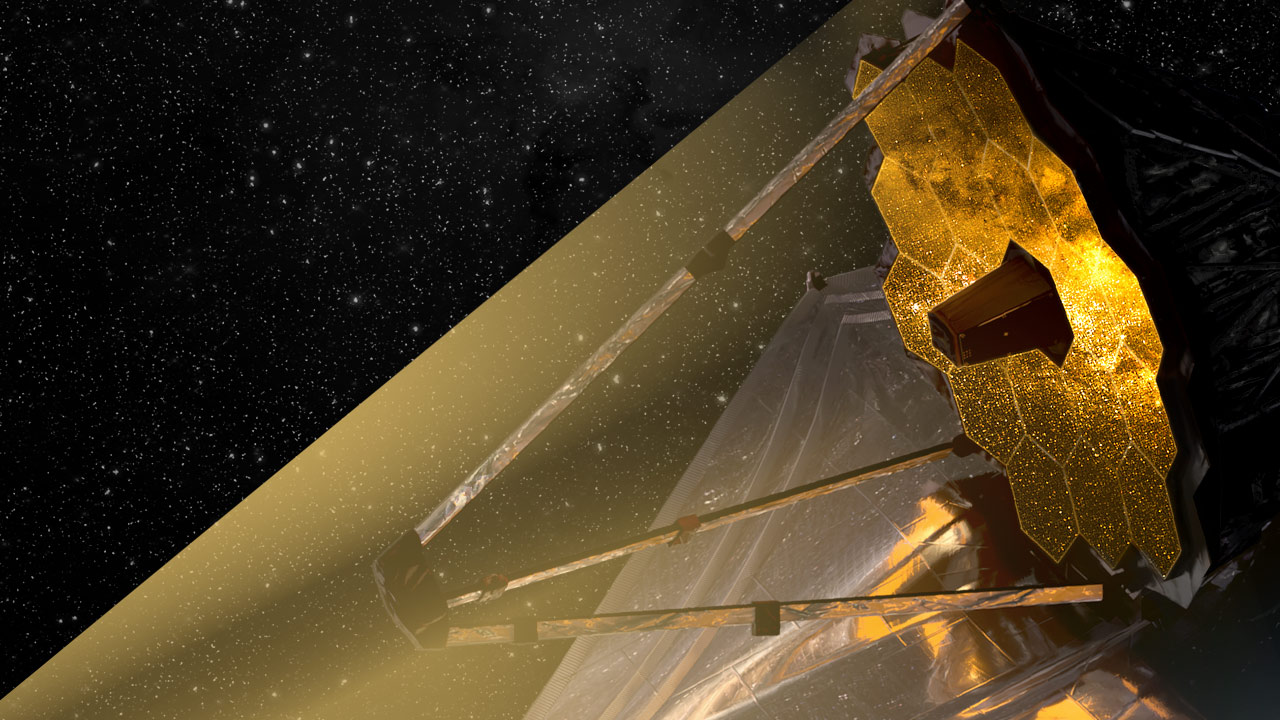
James Webb Space Telescope
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a space-based infrared observatory led by NASA with contributions from the European Space Agency and the Canadian Space Agency. Launched on December 25, 2021, it operates in a halo orbit around the Sun–Earth L2 Lagrange point about 1.5 million kilometers from Earth to study the early universe, galaxy evolution, star and planet formation, and exoplanet atmospheres. JWST’s 6.5-meter segmented, gold-coated beryllium mirror and five‑layer sunshield enable unprecedented sensitivity from 0.6 to 28.5 microns.
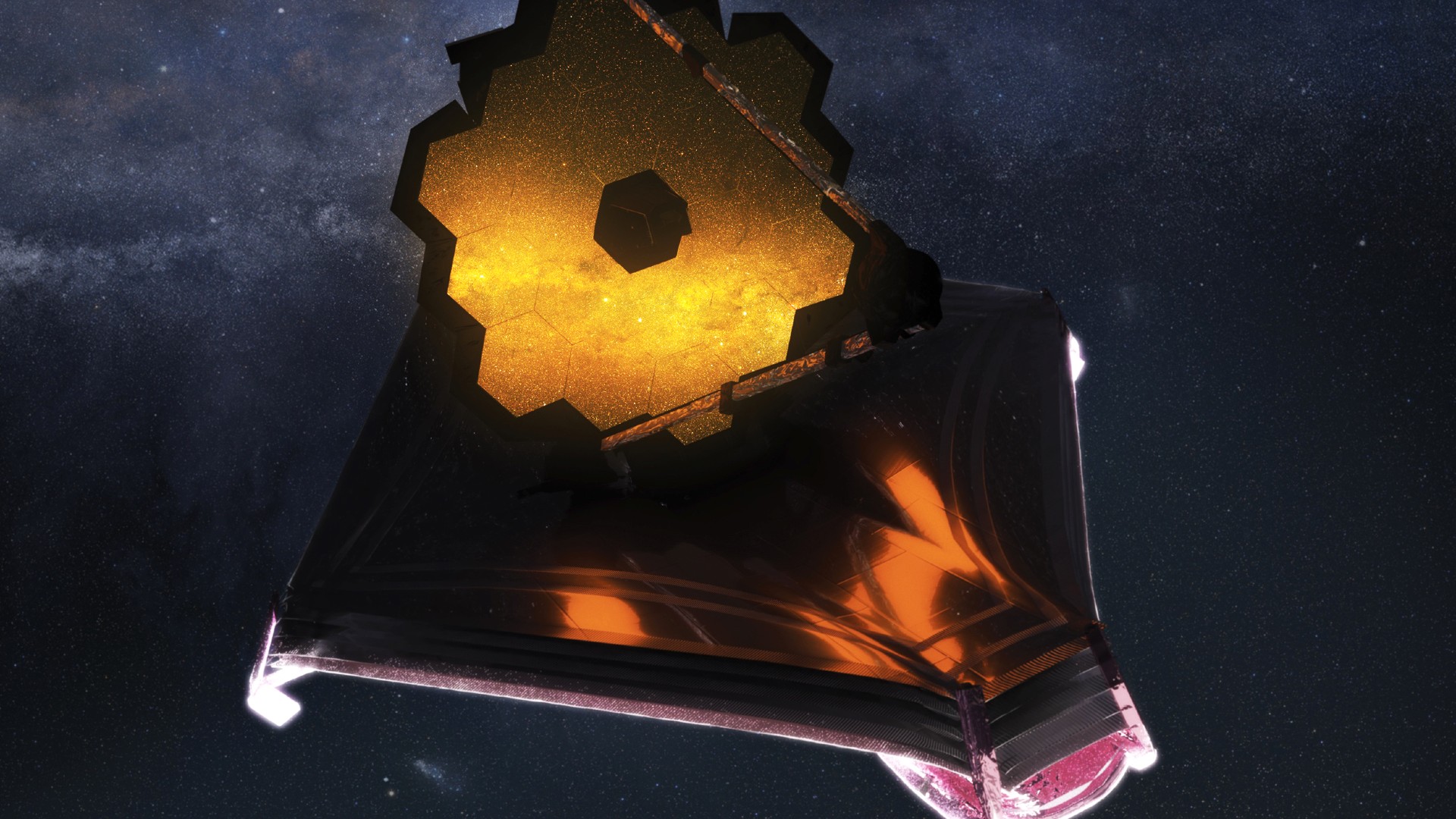

James Webb Space Telescope
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a space-based observatory launched in December 2021, designed to conduct infrared astronomy and explore the universe's earliest epochs, galaxy formation, star development, and exoplanet atmospheres.
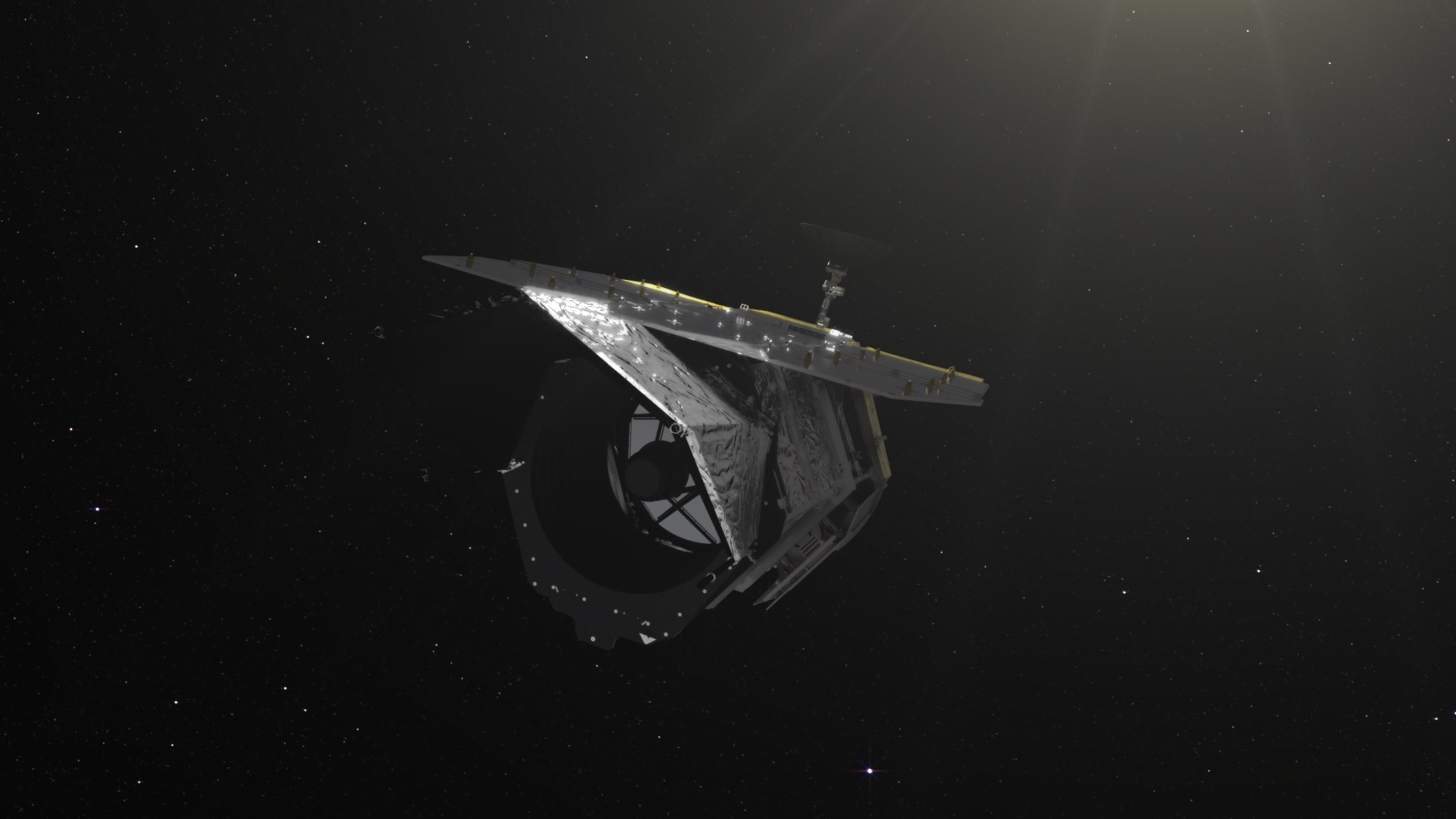

Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope
The Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope is a NASA flagship infrared observatory designed to investigate dark energy, conduct wide-field astrophysical surveys, and advance exoplanet science. Managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center with major roles for the Space Telescope Science Institute, JPL, and Caltech/IPAC, Roman is planned to launch no later than May 2027 to a Sun–Earth L2 orbit and will carry the Wide Field Instrument and a technology‑demonstration Coronagraph Instrument.