Web Development
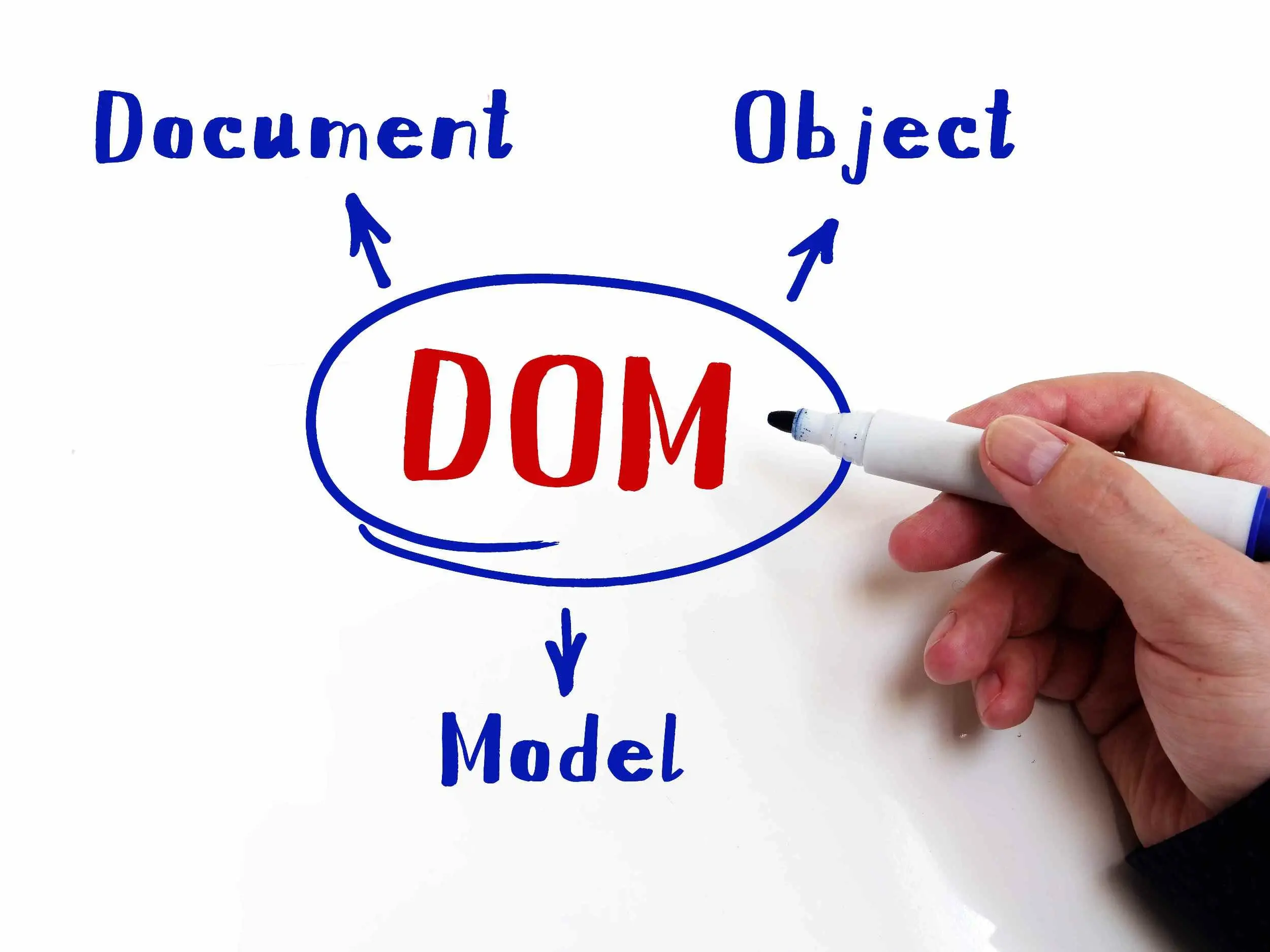
Document Object Model
The Document Object Model (DOM) is a platform- and language-neutral interface that represents documents as a tree of nodes and defines how programs access and manipulate that structure. It underpins dynamic behavior on the web, enabling scripts to read, modify, and react to changes in HTML, SVG, and XML documents across web browsers and other environments.

HTML
HyperText Markup Language (HTML) is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It forms the basic structure of web pages and is a cornerstone technology of the World Wide Web, alongside CSS for presentation and JavaScript for interactivity.

JavaScript
JavaScript is a high-level, interpreted (or just-in-time compiled) programming language that conforms to the ECMAScript specification. It is a core technology of the World Wide Web, alongside HTML and CSS, and is used by the vast majority of websites for client-side page behavior. As a multi-paradigm language, it supports event-driven, functional, and imperative programming styles.